


Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) levels are creeping up at some landfills, especially those that take C&D waste; some are seeing concentrations in the thousands to 30,000 parts per million (up from about 20 to 40 ppm ten years ago). And even at very low concentrations, H2S can be problematic.
Material Recovery Facility residuals, which typically contain significant amounts of pulverized drywall, are high in gypsum and sulfate. Once broken down, residuals become a high-surface-area material, leaching into and spreading through waste. When reacting with water and organics, it can potentially generate H2S. With a drive to divert more C&D debris, and regulations tightening around H2S, operators’ jobs get harder as they work to stave off emissions from this corrosive, flammable compound notorious for its “rotten egg” odor.
When building out their gas collection systems, controlling H2S becomes even more daunting. Sol Sim, an SCS Engineers Vice President, explains, “We see H2S concentrations jump when we expand landfill gas collection systems, often in cells that contain C&D residual screening materials. The gas was there all along but sequestered. Now it’s coming out of the ground, and the onset of issues can spike suddenly.”
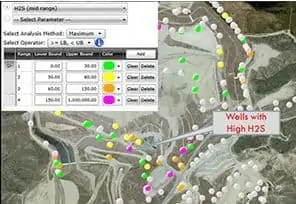
When spikes come on quickly, Sim’s team implements turnkey interim treatment approaches. They start by identifying the gas collection wells with the highest contributors and act fast to get them into compliance.
SCS teams take a two-pronged approach by stepping back and thinking about the big picture while taking action. It provides a major advantage to moving too quickly.
The more data, the better. Your engineers can simulate treatment with various media to assess the impact on flare inlet concentrations. And knowing potential impact at the flare is critical; it’s the compliance point where regulators measure sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions.
SO2 can’t be controlled through combustion, so removing H2S from waste before sending gas to the flare is essential. Sim thinks back to problems he’s investigated for clients who had SO2 sneak up on them, causing failed sulfur dioxide emissions testing.
The proactive measure of identifying problematic gas wells and treating them is key to staying in compliance. And Sim often finds clients using interim solutions as long as they can. He has seen them work well for up to five years but they don’t resolve operators’ long-term issues, which will become more challenging as our waste streams continue to change or as landfills continue to accept more and more C&D materials.

“We’re going to investigate thoroughly to pinpoint and understand the cause, but we do take immediate action in the interim. As part of the solution, we’ll develop an informed strategy to prevent issues well into the future,” he says.
For the longer haul, it takes time to get building permits. Coming up with permanent engineering designs and treatments requires a lot of troubleshooting and research. Even once engineers identify a lasting fix, it takes time to manufacture and install larger vessels and other infrastructure.
But they don’t wait for all these pieces to come together to act.
The priority is getting operators in compliance right away or taking down emissions if they are on the verge of noncompliance. As work begins, operators can breathe a little easier knowing they have time to figure out how to allocate resources and funds to implement a more permanent strategy.
“We’ve seen where data we’ve gathered while working on the immediate problem enables our clients to gain insight to make good decisions around rightsizing their infrastructure moving forward,” Sim says.
Watch and study while addressing the immediate problem.
Sim emphasizes that operators should not be surprised or act too quickly when they turn on the gas extraction system and see spikes in H2S concentrations. There is usually an initial spike from a new high H2S producing area at the onset of gas collection. He has seen operators abruptly stop extracting, which can lead to odors or other compliance issues.
“When you put in a treatment system, you can take out the initial surge in H2S to allow time for the concentrations to level out. It’s important to allow that window for initial surges to run their course to understand the problem better. Otherwise, you could over-design your system around a short-term event,” Sim advises.
He points to a real-life scenario: a site that skipped the interim step of starting with a less expensive initial solution. Once they started drawing on the gas, they realized the problem was not as substantial as originally thought, and they didn’t need a multi-million-dollar system in the end.
A balancing act.
“Imagine H2S generation as an expanding balloon; if you pop it, air rushes out fast [akin to when you first pull gas from the ground]. That concentration level scares people. But if you react by shutting off extraction points, your balloon will continue to expand and eventually create odor problems. The goal is to extract the gas and H2S at the rate it is being generated, so it’s a balancing act, where expertise and technology both play key roles,” Sim says.
Early work typically begins by identifying wells that are the highest contributors and concentrating efforts there. It’s a complex process as sites can have fifty to thousands of collection points. Having the historical data and saving the data to watch the trend makes identifying and analyzing specific wells or clusters much more efficient.
Successfully attacking those high offenders requires an understanding of flow and concentrations. After locating the problem area, Sim takes samples using Dräger tubes at strategic points throughout individual wells and headers to identify concentrations. Gas well monitoring and the corresponding flow data will tell you if you’ve taken emissions down sufficiently.
More Resources:
SCSeTools Landfill Data Monitoring and Analysis
Staying Ahead of Odor Management at Solid Waste Facilities
Landfill data collection and analysis are more tactical than ever, and landfill technology provides methods to manage and use the data to create efficiencies. With the implementation of the NESHAP, NSPS/EG requirements, Landfill Operators will monitor more often and maintain more records. Data collection mechanisms will likely broaden soon to include drone and satellite data collection as acceptable for agency requirements.
Our September 23, 2021, SCS’s Client Webinar focuses on landfill gas maintenance and how Operators find efficiencies by monitoring and collecting LFG data. Using SCS eTools, the webinar includes common scenarios at landfills and answers several questions, including:
Demonstrations include:
SCS Engineers announces its iOS and Android application SCS WDT™ for wireless data transfer of landfill flare readings to mobile devices. The app expands the power of SCS MobileTools® to observe system and environmental activity securely and in real-time.
Today’s landfill gas flares collect data using a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system. The flare’s SCADA system records data at preset intervals generating hundreds of thousands of readings to process and analyze. Often data is stored on a data card at the flare site. A technician collects the data by transcribing it into a log or digitally reading it, then transferring the reading to a computer. The data is then uploaded into the landfill’s database for analysis and reporting.
The process, with its multiple steps, is slow and open to human error. SCS WDT™ digitally collects flare readings directly into a mobile device and into SCS DataServices® in seconds, reducing human error and multiple steps. The app’s interface provides secure access to information that drives critical operating decisions and collects historical data for trends, corporate directives, and landfill gas OM&M programs.
Landfill managers and environmental engineers can monitor their flares in real-time, seeing exceedances immediately. SCS WDT™ uses GPS to capture the exact physical location of flares and place the data into the appropriate landfill’s site location too. Flare readings are available, literally in seconds, for review, analysis, and corrective action if needed. Pilot testing at 30 landfills nationwide demonstrates that SCS WDT™ saves time and errors by removing extra steps and people in the progression; there is no need to wait until the end of a technician’s shift to transfer readings or have extra hands in the process.
SCS DataServices®, a secure web-based landfill gas management application, is part of the SCSeTools® platform in use on hundreds of landfills backed by over 50 years of landfill design, operation, and maintenance experience. SCS Engineers understands how unique landfill operations are today, so SCS WDT™ works as a standalone app with other platforms and is free to SCSeTools® users. Download on the Apple App Store for iPhones and iPads, Google Play for Android.
The SCSeTools® platform and applications help facilities operate more efficiently by continually gauging operational health and spot trends that help determine when and how to invest in infrastructure. For additional information and demonstrations of these productivity-enhancing tools, please click here.
The unsung hero at landfills with a landfill gas collection system is the humble Wellfield Technician. The position of Wellfield Technician is multifaceted; this individual needs to be well equipped to deal with constant changes. A good technician is capable of:
All while communicating effectively with those on their team, during all kinds of weather and changing conditions.
One practice that most good Technicians embrace is keeping effective field notes. Those not engaging in this practice should consider doing so. Field notes and comments added to a row of monitoring data can be of great future value to the technician and the rest of the team. Accurate and detailed field notes contain information that can help the project team when it comes time to diagnose, repair, or troubleshoot various wellfield issues.
Whether it’s a handwritten entry in a logbook, a comment stored in a field instrument, or notes saved in a smartphone, tablet, or computer, the information recorded in field notes is indispensable for the proper, efficient maintenance of the wellfield.
Technicians are hard-pressed to recall every detail during the hectic daily push to get the wellfield read, while multitasking and keeping up with items that pop up at a moment’s notice. By keeping track of this information through note-taking or SCSeTools®, the technician can be more efficient over time – they won’t be scratching their head, trying to remember a detail important to a task.
Examples of items we track in our database include: wellhead valve positions, surging in vacuum supply risers at wellheads, required maintenance of sample ports, flex hoses, audible wellhead leaks, ponding water around wells, surface cracks around a well, and borehole backfill material settlement.
Regardless of how recorded, save field notes as valuable points of reference.
Handwritten notes are entered into a preventative maintenance program or a wellfield database so that they are accessible for use in planning repairs or troubleshooting problems. Another option is to capture them automatically, even noting the GSI coordinates into a database such as SCSeTools, to save time and lessen transcription errors.
Once completing wellfield monitoring and tuning, technicians then use comments or notes as a punch-list to return to the wellfield − ready to perform maintenance or repairs. These are the actions that keep the landfill gas collection components operating efficiently, and clients’ happy.

Learn more about Landfill Services here.
On October 11, SCS Engineers’ David Hostetter and Phil Carrillo present several case studies during the webinar demonstrating how Remote Control Monitoring (RMC) has lifted the burden of data collection and facilitates the review and analysis of data for use in decision-making.
In this webinar, several case studies regarding remote monitoring and control (RMC) systems for landfill gas and leachate systems will be presented. This includes a description of integrated systems which are used for data collection and analysis and how they were used to identify, troubleshoot and solve real problems in an effective and efficient manner.SCS recognized this as an issue in the industry and developed systems to streamline the process using the latest technology to help perform routine, sometimes complex, data analysis, and to automatically push reports and alerts to operators, engineers, and project managers. This has been a dramatic change that removes human error while reviewing pages of data and allows people to focus on what really matters.
RMC systems give the ability to:
Watch Dave’s video here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pYezcobr1Cg
Dave explains how landfill owners/operators use SCS RMC® to view, operate, and control field equipment. The presentation covers how SCS RMC® helps to reduce operating costs – sending technicians to respond when necessary to alerts from flare systems, leachate systems, and air quality sensors. SCS helps manage all field resources and personnel better while enhancing reporting and data management too.
Over years of working on operations and maintenance of landfill gas collection and control systems and leachate management systems, SCS found that too many times data is collected and no one has the time to review and analyze it for improved decision-making.
As an industry-wide issue, SCS developed systems to streamline the process using technology and our field expertise to help perform routine and sometimes complex data analysis and to automatically push reports and alerts to operators, engineers, and project managers.
The improvements are dramatic; by removing human error from reviewing pages of data we now focus our time and energy on what really matters, using what the data tells us to make informed decisions. Let’s put the technology into the context of everyday operations – identify, troubleshoot, and solve landfill gas and leachate challenges.
This SCS paper illustrates several sites using integrated systems for data collection and analysis and how they are used to identify, troubleshoot, and solve real problems in an effective and efficient manner.
Privately share this article using the email icon on the left navigation bar. Print the article using the Download icon just under the article, or your browser commands.
About the Authors:
David P. Hostetter, PE, Denver, Pennsylvania
Phil Carrillo, Huntington Beach, California
Darrin D. Dillah, Ph.D., PE, BCEE, Reston, Virginia
SCSeTools® gives you the ability to instantly map air leaks, vacuum distribution, wells that are “over pulling” and wells that are underutilized – valuable tools for every wellfield technician to maximize system performance beyond simple compliance tracking and reactive wellhead tuning.
As a field technician, you walk a fine line – tuning to a threshold, pulling as hard as you can, as safe as you can. When important data factors start to wander you need to troubleshoot quickly to keep collecting as much as gas as possible without over compensating and adjusting wellheads multiple times. SCSeTools® makes troubleshooting faster and more efficient by turning your data into maps identifying important conditions in the field and the wellheads that need tuning. Field technicians know how to balance the wellfield without killing bacteria and without diluting the gas.
A map of your field with your specific tuning range quickly shows data that are typically missed in reams of data. SCSeTools alerts you to these indicators using a map of each wellhead in the wellfield. Where you formerly needed months for these changes to become apparent, SCSeTools tells you at the touch of a button when a change began occurring and which wellheads are impacted. As a technician you know what you need to tune and which wellheads need your attention.
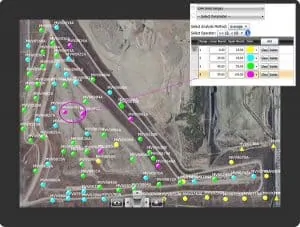
Using SCSeTools pick any parameter that the GEM collects and create custom ranges or use specified guidelines to quickly identify trends throughout the landfill. Tuning ranges can be adjusted to specific conditions found at individual landfills. Smooth a saw tooth collection pattern and learn from your data for maximum vacuum and maximum collection without risk.
“Our clients enable SCS to build, grow, and sustain an engineering firm dedicated to solving environmental challenges,” said Jim Walsh, President and CEO of SCS. “We sincerely thank our friends, colleagues and, in particular, our clients for helping us achieve a highly regarded ranking each year.”
Firms are ranked in terms of revenue by Engineering News-Record magazine (ENR), as reported in the May 2, 2016, issue of the “ENR Top 500 Design Firms Sourcebook.” SCS has made the Top 500 list since its publication in 2002 and has ranked in the top 100 of that list since 2008.
When sorted by firm type, SCS Engineers is ranked the second largest environmental engineering firm (ENV) and is ranked in the “Top 20 Sewerage and Solid Waste” service firms in the nation. SCS has made this top 20 list since 2002.
Later in the year, ENR will publish additional resources and lists, including the “Top 200 Environmental Firms” issue, typically published in the month of August.
Learn more about our latest innovation, SCSeTools

Long story short, an escapee from San Quentin and any uncontrolled methane air molecule may be more similar than we may presume. In fact, a common LDAR practice is to use an infrared imaging camera; similar to the camera often used in search of fugitive criminals.
On a serious note, fugitive emissions are something that both industry and regulators have been focused on for decades, and the past and present efforts made to limit them are no less than remarkable.
Specific to Onshore Oil and Gas Exploration & Production, the Federal Regulations applicable to fugitive emissions are fairly young. Finalized in 2012, NSPS OOOO is no longer a toddler and is in the middle of growing into NSPS OOOOa (Public Comment Deadline March 11, 2016). On a national scale, NSPS OOOOa will expand fugitive emission monitoring and control requirements (VOC’s and methane) to several facility types associated with the industry and is expected to be finalized before the close of 2016.
In California, fugitive emissions from Onshore Oil and Gas Exploration & Production have been regulated for a long time. In fact, the O&G industry in Santa Barbara County has dealt with fugitive emission requirements since 1979. Since then SCS Engineers has been assisting with fugitive emission monitoring for our valued clients. Today, SCS Engineers provides the Oil and Gas Exploration and Production industry with efficient and effective LDAR services.
So fear not, SCS Engineers is ready to supply the knowledge and skill set you need to stay compliant, maintain your operations, and respect your bottom line. Remember, unless the doors are closed, pumps are turned off, and equipment is flushed and plugged; fugitive emissions requirements and LDAR will likely still apply.
Applicability: Determining Federal vs. State oversight is the first step. Non-Major Source Oil and Gas Production facilities are either subject to NSPS OOOO (soon to be OOOOa) or a related State specific rule (i.e. Colorado Regulation 7). Once oversight is determined, then there may still be exemptions for your facility (i.e. facility constructed before August 23, 2011). And finally, once regulatory oversight is confirmed and you determine that LDAR is required for your facility, then the last step is to figure out which equipment is applicable (i.e. VOC content > 10% by weight). Basically, an applicability determination can be daunting.
Equipment: EPA’s Method 21 is historically and currently referenced in all LDAR regulations. Method 21 requires an instrument such as the Flame Ionization Detector (FID) or Photo Ionization Detector (PID). More recently the Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) Camera has been included in LDAR regulations and utilized in LDAR programs. Presently, there are several instrument technologies that exist and are in the works, but not yet mainstream in Oil and Gas sector. Ultimately, if you were to find yourself conducting LDAR monitoring at your oil and gas facility tomorrow per an established regulation, you would most likely need to use an FID or OGI.
Recordkeeping: Personally, I like the simplicity of using paper forms for field notes; however, the old-fashioned way comes with risk. The up-front and ongoing data involved with an LDAR program is too much for maintaining a paper to computer process, regardless of how organized you think you are. Therefore, a computer database platform is recommended and necessary for managing your LDAR recordkeeping. Beyond just recordkeeping, a database platform can organize schedules, alerts, generate reports, extract trends, and many other applications to help keep your LDAR program compliant. One such platform worth considering is SCSeTools™. This cloud-based software can provide the database capabilities used on the desktop, but almost more importantly, provides mobile data input capabilities with the SCS MobileTools™ application fit for Android and IOS systems. Keep the fugitives from escaping, and document containment for the authorities!

Whether you want to discuss LDAR or Dodger baseball, don’t hesitate to contact me, or SCS Engineers.
Resources:
Learn more on the SCS service pages and read SCS project case studies from across the nation to help fine tune your program.
Outside links to the EPA proposed rulemaking website:
Technical bulletins provide salient information in a condensed format. These summaries are useful to understand and start to plan for potential impacts to your business. Both bulletins posted today include deadlines and additional resources with contact information to help answer your questions. The two bulletins posted today are as follows:
Clicking the title of each Technical Bulletin will take you to the full text. Each Bulletin may be shared, emailed, or printed.
About Pat Sullivan:

Pat Sullivan, BCES, CPP, REPA, is a Senior Vice President of SCS Engineers and our National Expert on the Landfill Clean Air Act and the New Source Performance Standard (NSPS). Mr. Sullivan has over 25 years of environmental engineering experience, specializing in solid and hazardous waste-related issues.
Click on Pat’s name to see his full qualifications and experience.