

Accumulating liquids are problematic for landfills taking sludges and other wet wastes not traditionally part of the incoming waste stream. Add to the mix increasing precipitation, and operators could be staring down the perfect storm—especially as they work to optimize their gas extraction systems. Here’s the challenge, explains Pete Carrico, SCS Engineers Senior Vice President and national expert on liquids management:
“Trash is porous, and the soils used for daily and intermediate cover usually aren’t, so liquid gets trapped between alternating trash layers as the landfill fills. These “perched” liquids can drain into well columns and block the slotted portion of the extraction well piping that withdraws gas from waste and into the gas collection system.”
Even a robust vacuum on the wells will not pull gas once pipes fill with fluid. With no path to move it from trash into the collection infrastructure, operators work harder to stave off odor and slope stability issues, among potential resulting problems.
The good news is they have a recourse to remove the liquids, unblock well perforations, and extract more gas. They do it by installing dewatering systems: an intricate network of pneumatic pumps, air lines to power them, and conveyance lines, also known as force mains, to remove liquid.
Manufacturers have designed and redesigned their pumps to try and address problems specific to landfill gas extraction systems. And the equipment does the job but requires meticulous attention and skill to keep all the moving parts going. These liquids are rough on pumps due to their harsh nature. The suspended solids and biological material they contain are the biggest challenges, and if the landfill has high temperatures, these liquids can heat up, further taxing the system, Carrico says.
“No pump indefinitely survives the challenging conditions you have in landfills. So, where we can make the biggest difference is with these maintenance programs,” Carrico says. You’re spending O&M budget on what provides the most impact.”
SCS uses dedicated, factory-trained pump crews who focus solely on operating and maintaining gas extraction dewatering systems. These crews help ensure the infrastructure functions as it should, and gas moves through well piping slots, into the gas header piping, and to the blower/flare station for beneficial end-use.
“Operations run more smoothly with these crews in place. An SCS field crew is as unique as each landfill. Our specialists have various skill sets, i.e., gas collection system monitoring, surface emissions monitoring, or pump maintenance expertise. That’s how we produce better outcomes in terms of pump performance. If you effectively maintain and repair the pumps, you will restore them to their designed specifications, pump more liquids, and with greater ease,” Carrico says.
The teams, who work on landfills across the country, stay busy. One site can have five to 300-plus pumps, each with multiple components, and they must be removed and cleaned frequently.
Replacing worn, fouled, or damaged components is an especially tedious and complex job.
Some wells are 70 to 100 feet deep. Pulling air lines, liquid lines, and pumps out from that depth is hard and requires special equipment to do safely. SCS crews know how to take them apart and put them back together; they don’t just lower them back in the ground after working on them. But hook them up to air and water lines and watch them work at capacity before returning them to service.
It’s a value add; with a good maintenance plan and the right crew, pumps can be kept at their designed specifications and run efficiently for many years. They can typically be cleaned and reset for a fraction of their replacement cost.
“We leverage our size and resources. We have a deep bench of in-house experts and engineers willing to share information to help with problems, which is important as conditions vary at each site, as can problems and solutions. So, it’s important not to do this in a silo but rather pull from our broader knowledge base,” Carrico says.
Technology helps too, especially with tracking, maintaining, and reporting progress to clients. A geographical information system (GIS) maps each well’s location, and pump technicians upload data corresponding to each one from wireless tablets almost instantaneously.
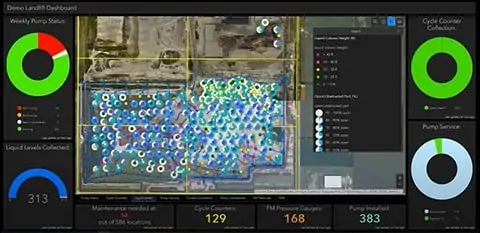
The ability to automate tracking and display critical information right away on a dashboard has increased our program’s efficiency. Technicians spend less time tracking and look at analyses of all the landfill conditions to know where to concentrate their efforts, Carrico says.
A few landfills are working to avoid pumping liquids altogether. They are building large gabion rock structures at the landfill’s base, with piping that connects to the extraction well system, creating a conduit. Liquids automatically drain to the bottom where leachate is intended to go while effectively pulling more gas into the gas collection system.
“This is a newer trend that some of our clients are already doing. And we are involved supporting the well designs,” Carrico says.
For now, in most cases, achieving the best outcomes is about investing in pumps and a good maintenance program.
“Monitoring and regularly measuring—checking stroke-counters, which show how many times a pump cycles, and checking flow meters to know how many gallons a day a system produces are key to finding savings. It’s how you reduce or prevent catastrophic failures,” says Greg Hansen, Senior Project Manager with SCS Field Services Operations, Maintenance & Monitoring.
To execute properly, Hansen provides this advice for operators setting up a pump program:
Have pump maintenance areas with water, electricity, disposal means for waste liquids, and storage facilities for spare parts and tools. More specifically:
Operators planning on doing maintenance in-house should train their technicians on cleaning, servicing, and testing pumps. Either SCS or the pump manufacturer can provide this training.
Above all, Hansen says, “You need a comprehensive OM&M program. The better the job tuning pumps, the better they do in the field, and the longer they work before being cleaned or repaired. It’s a continual process.”
More Resources
An essential part of landfills accepting organic matter is the gas collection and control system (GCCS) for controlling odors and landfill gas (LFG) emissions into the environment; the piping network. GCCS design and construction have evolved significantly over the past four decades, from passive venting trench systems to a sophisticated and elaborate piping systems with specialized components for handling LFG, landfill liquids, and condensate flowing through the piping network.
This detailed article discusses best practices and recommendations that GCCS designers keep in mind; careful attention to these details can potentially save landfill operators significant modification costs and inconveniences prior to and during construction of the final covers.
Read the full article published in MSW Magazine.
About the Authors: Ali Khatami, Ph.D., PE, LEP, CGC, is a Project Director and a Vice President of SCS Engineers. Srividhya Viswanathan, PE, is a Senior Project Manager with over 10 years of engineering experience. David Fisher is an SCS National OM&M Compliance Manager with 18 years of environmental experience.
We continue SCS’s Advice from the Field blog series with guidance from an article in MSW Magazine by Daniel R. Cooper, Jason Timmons, and Stephanie Liptak.
The authors of a recent article in MSW Management Magazine present engineering ideas that provide for more efficient construction of a GCCS. Gas system operators will benefit by having fewer pumps to operate and maintain and shallower headers that are more easily accessible. Odor management will be easier along with other benefits.
Read the full article here to learn about the design elements for maximizing long-term benefits, impacting: bottom liners, location of the blower/flare station, leachate risers, extraction well targets, and external header piping.
Landfill operators are making significant investments developing comprehensive lining systems to protect human health and the environment. These lining systems are normally equipped with drainage layers to convey leachate reaching the lining system to collection pipes and sumps for removal from the landfill. Landfill operators are also heavily investing in collecting and removing landfill gas for disposal or conversion to renewable energy.
After three decades of experience with these systems, landfill liquids may still accumulate in some gas wells adversely impacting gas removal efficiencies. In these situations installing a pneumatic submersible pump in the gas well to lower the liquid head in the well, restoring gas removal efficiencies is standard practice. However, this remediation technique requires additional capital investment.
An Alternative Solution Exists
A more recent alternative, constructing vertical drains from the bottom up where gas wells are located, may be a better solution. Construction of a vertical drain/gas well begins by constructing a gravel pad at the bottom of the landfill after completion of the lining system and placement of the protective soil cover over the lining system. The gravel pad may be 15 ft. by 15 ft. in lateral dimensions by 10 ft. in height. Gravel pads are normally constructed where future vertical wells are planned to be drilled. The center of each pad is surveyed, and the information is used to locate future gas wells at some vertical distance above waste that is placed in the new cell over time. The gas well drilling continues until it reaches the gravel pad at the bottom of the landfill. The connection between the gas well gravel pack and the gravel pad at the bottom makes it possible for landfill liquids to flow down and drain directly into the leachate collection system below the gas well.
Vertical drains help landfill liquids reaching the gas well gravel pack to flow to the leachate collection system at the bottom of the landfill; thus preventing watering out the gas wells. This sustainable alternative keeps gas production efficient and is environmentally sound, requiring less capital investment.
About the Author: Dr. Ali Khatami
More information about Liquids Management and Landfill Engineering
Related Advice, Whitepapers, and Articles
SCSeTools® gives you the ability to instantly map air leaks, vacuum distribution, wells that are “over pulling” and wells that are underutilized – valuable tools for every wellfield technician to maximize system performance beyond simple compliance tracking and reactive wellhead tuning.
As a field technician, you walk a fine line – tuning to a threshold, pulling as hard as you can, as safe as you can. When important data factors start to wander you need to troubleshoot quickly to keep collecting as much as gas as possible without over compensating and adjusting wellheads multiple times. SCSeTools® makes troubleshooting faster and more efficient by turning your data into maps identifying important conditions in the field and the wellheads that need tuning. Field technicians know how to balance the wellfield without killing bacteria and without diluting the gas.
A map of your field with your specific tuning range quickly shows data that are typically missed in reams of data. SCSeTools alerts you to these indicators using a map of each wellhead in the wellfield. Where you formerly needed months for these changes to become apparent, SCSeTools tells you at the touch of a button when a change began occurring and which wellheads are impacted. As a technician you know what you need to tune and which wellheads need your attention.
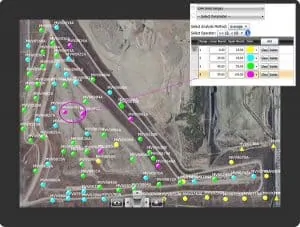
Using SCSeTools pick any parameter that the GEM collects and create custom ranges or use specified guidelines to quickly identify trends throughout the landfill. Tuning ranges can be adjusted to specific conditions found at individual landfills. Smooth a saw tooth collection pattern and learn from your data for maximum vacuum and maximum collection without risk.