

SCSeTools® – Developed by Landfill Gas Practitioners for Landfill Owners and Operators
The Birth of LFG Data Tracking
In the early 2000s tracking landfill gas data at facilities was anything but uniform, organized, or secure. The industry was using various methods to track data on paper forms and logbooks, then transferring it by hand into spreadsheets. Some of us used desktop database applications, but as the saying goes, necessity is the mother of invention.
From an SCS employee’s idea for demonstrating how to use landfill gas monitoring data to analyze and pinpoint system corrections, SCS DataServices® was born. In the span of several months, a team of SCS’s landfill engineers, field technicians, and technology gurus worked with client-needs to create a concept application visualizing collected landfill data on maps. Our staff field-tested it with good results, and SCS Field Services began using the application to visualize issues with wellfields that aren’t readily apparent when looking at spreadsheets.
A large SCS landfill client had seen our field staff using DataServices, asked if SCS would consider providing them with access to the application on a subscription basis. Our team adapted DataServices, added features, and continued improvements tailored for the client’s use.
As soon as secure data transfer became feasible, SCS moved to an Internet-based solution for our landfill gas practitioners. The platform called SCSeTools® holds the data collected by SCS DataServices®.
Applications and features roll out as we continually update and upgrade, incorporating ideas and improvements from our users and staff along the way. DataServices is addressing the landfill gas management needs of over 600 landfills across the US and Canada in 2021.
The keys to success follow our mission and values of maintaining close communications with our clients, field staff, engineers, and eTools support staff (all landfill gas practitioners), with the help of software engineers. Technology companies are not up at night thinking about landfill operations, but we are.
We introduce our SCS eTools landfill technology capabilities and a few of the creative and talented SCSers behind the technology in the next segment. Our speakers walk you through demonstrations of how over one-third of the landfill owners and operators in North America are increasing efficiencies using SCS eTools.
Visualizing Landfill Challenges – Shortcuts to Keeping Your Wellfield in Balance
DataServices shows the entire wellfield for any monitored parameters and zooms in on troublesome areas or wells. Results can be as simple or detailed as the landfill owners’ environmental and business needs dictate. The detailed examples here illustrate how graphs, maps, and charts help keep the wellfield in balance. We link each challenge to the description of a video demonstration.
In balance means extracting more gas for renewable energy, preventing odors and methane migration, keeps subsurface and surface conditions and workers safe. The information can help diagnose equipment conditions before they become costly, maintain regulatory compliance, and support cost estimates if the landfill is expanding or more infrastructure investment or equipment is needed.
Looking at vacuum distribution across a gas collection system – Select the system pressure map, which highlights vacuum distribution across the wellfield to show the wells with good (expected) vacuum, pressure drop over distance, and any wells unexpectantly losing vacuum. Zooming in and changing the vacuum ranges further enhances where to assign staff to troubleshoot any identified issues.
Using a methane distribution map shows whether the wells are tuned to where the landfill owner wants them. Wells may be identified below the targeted range, indicating slight over pulling; a technician can use this map to identify such issues and quickly check the identified wells. Wells identified above the desired methane tuning range indicate wells not collecting enough gas, which has consequences. These wells can be the source of odors, leachate seeps, possible lateral migration to an out of waste probe. Not sending enough fuel to a power plant or atmospheric releases can affect surface emissions monitoring.
Managing liquids – Changing waste streams and more rainfall in certain areas of the country complicates liquids management. DataServices visualizes the impacts of liquids on wells and helps landfill owners better manage a proper liquids removal program. The program will let them know how many pumps to budget for and, over time, where to relocate well dewatering pumps so that they are most efficient at removing liquids from landfills.
High-BTU Gas Plants –Filter maps help users locate wells contributing to gas dilution into renewable energy plants. It can help create punch lists for landfill staff to investigate, troubleshoot and tune. As wellfield technicians make corrections, they show on the map in real-time.
Temperature and subsurface oxidation events – Some call the condition subsurface fires, but this is a serious issue for landfills. Over-pulling wells, damaged infrastructure, and other conditions can cause oxidation events. Using a combination of temperature Parameter Maps to review wellhead temperature distribution and a Points Chart feature provides a deeper dive into the data. It provides more insight into which well or wells may be contributing to the high-temperature issues.
Locating a specific well – That’s not so easy when hundreds of wells surround you and at larger landfills. DataServices had built-in filter features to identify a single monitoring point on a wellfield map easily.
Customizing for compliance, best practices, and rules – DataServices allows monitoring points across a single site to have customized rules for each monitoring point. Rules can be for regulatory purposes, standard operating procedures, best management practices, and even site-specific preferences or any combination thereof. It is efficient to customize rule application to landfills and collection points – meaning wells, probes or ports, horizontal collectors. This customization capability helps organize and confirm regulatory compliance. It is especially salient with the 2021 EPA and state compliance changes for a single landfill or an organization with hundreds of landfills.
MobileForms – Inspection forms, blower flare station monitoring forms, load tracking from municipalities, incoming hazardous waste tracking, MRF bale counts are examples of paperless entry available. The data feeds directly from mobile phones to the supervisor and into the maintenance department, so staff can start cataloging and looking at what’s going on in real-time at several types of facilities. It’s available for regulators and inspections and helps reduce staff hours tabulating and centralizing the information. Any information historically captured on a form or log attached to a clipboard can now be captured and stored electronically. From there, it can be recovered and produced as a PDF export file or data from the forms used to trend data and help make informed operational decisions.
MobileTools – DataServices in a condensed format suitable for mobile devices. Field staff use MobileTools to save time formerly used to return to the office, transfer/transcribe the collected data and upload it to a supervisor for quality checks before storage. Technicians can now recall the last 20 readings for any given well and review trend graphs on their phones or tablets while standing adjacent to the well they have questions about and need to access the data. MobileTools also allows them to upload field data such as liquid level readings while the data is being collected. The information instantly populates into DataServices and is available for review by others on the project team.
The most valuable tools are in development now for release in 2022. ARC GIS integration developed under SCS RMC® will further enhance DataServices with even better visualization and location capabilities and provide enhanced features such as allowing landfill owners to see their well as-built information and view subsurface information about their wells.
Learn more at SCS Engineers, where we adopt our clients’ environmental challenges as our own.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) levels are creeping up at some landfills, especially those that take C&D waste; some are seeing concentrations in the thousands to 30,000 parts per million (up from about 20 to 40 ppm ten years ago). And even at very low concentrations, H2S can be problematic.
Material Recovery Facility residuals, which typically contain significant amounts of pulverized drywall, are high in gypsum and sulfate. Once broken down, residuals become a high-surface-area material, leaching into and spreading through waste. When reacting with water and organics, it can potentially generate H2S. With a drive to divert more C&D debris, and regulations tightening around H2S, operators’ jobs get harder as they work to stave off emissions from this corrosive, flammable compound notorious for its “rotten egg” odor.
When building out their gas collection systems, controlling H2S becomes even more daunting. Sol Sim, an SCS Engineers Vice President, explains, “We see H2S concentrations jump when we expand landfill gas collection systems, often in cells that contain C&D residual screening materials. The gas was there all along but sequestered. Now it’s coming out of the ground, and the onset of issues can spike suddenly.”
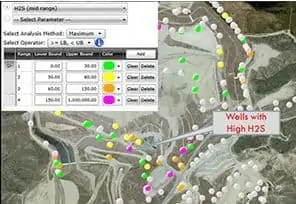
When spikes come on quickly, Sim’s team implements turnkey interim treatment approaches. They start by identifying the gas collection wells with the highest contributors and act fast to get them into compliance.
SCS teams take a two-pronged approach by stepping back and thinking about the big picture while taking action. It provides a major advantage to moving too quickly.
The more data, the better. Your engineers can simulate treatment with various media to assess the impact on flare inlet concentrations. And knowing potential impact at the flare is critical; it’s the compliance point where regulators measure sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions.
SO2 can’t be controlled through combustion, so removing H2S from waste before sending gas to the flare is essential. Sim thinks back to problems he’s investigated for clients who had SO2 sneak up on them, causing failed sulfur dioxide emissions testing.
The proactive measure of identifying problematic gas wells and treating them is key to staying in compliance. And Sim often finds clients using interim solutions as long as they can. He has seen them work well for up to five years but they don’t resolve operators’ long-term issues, which will become more challenging as our waste streams continue to change or as landfills continue to accept more and more C&D materials.

“We’re going to investigate thoroughly to pinpoint and understand the cause, but we do take immediate action in the interim. As part of the solution, we’ll develop an informed strategy to prevent issues well into the future,” he says.
For the longer haul, it takes time to get building permits. Coming up with permanent engineering designs and treatments requires a lot of troubleshooting and research. Even once engineers identify a lasting fix, it takes time to manufacture and install larger vessels and other infrastructure.
But they don’t wait for all these pieces to come together to act.
The priority is getting operators in compliance right away or taking down emissions if they are on the verge of noncompliance. As work begins, operators can breathe a little easier knowing they have time to figure out how to allocate resources and funds to implement a more permanent strategy.
“We’ve seen where data we’ve gathered while working on the immediate problem enables our clients to gain insight to make good decisions around rightsizing their infrastructure moving forward,” Sim says.
Watch and study while addressing the immediate problem.
Sim emphasizes that operators should not be surprised or act too quickly when they turn on the gas extraction system and see spikes in H2S concentrations. There is usually an initial spike from a new high H2S producing area at the onset of gas collection. He has seen operators abruptly stop extracting, which can lead to odors or other compliance issues.
“When you put in a treatment system, you can take out the initial surge in H2S to allow time for the concentrations to level out. It’s important to allow that window for initial surges to run their course to understand the problem better. Otherwise, you could over-design your system around a short-term event,” Sim advises.
He points to a real-life scenario: a site that skipped the interim step of starting with a less expensive initial solution. Once they started drawing on the gas, they realized the problem was not as substantial as originally thought, and they didn’t need a multi-million-dollar system in the end.
A balancing act.
“Imagine H2S generation as an expanding balloon; if you pop it, air rushes out fast [akin to when you first pull gas from the ground]. That concentration level scares people. But if you react by shutting off extraction points, your balloon will continue to expand and eventually create odor problems. The goal is to extract the gas and H2S at the rate it is being generated, so it’s a balancing act, where expertise and technology both play key roles,” Sim says.
Early work typically begins by identifying wells that are the highest contributors and concentrating efforts there. It’s a complex process as sites can have fifty to thousands of collection points. Having the historical data and saving the data to watch the trend makes identifying and analyzing specific wells or clusters much more efficient.
Successfully attacking those high offenders requires an understanding of flow and concentrations. After locating the problem area, Sim takes samples using Dräger tubes at strategic points throughout individual wells and headers to identify concentrations. Gas well monitoring and the corresponding flow data will tell you if you’ve taken emissions down sufficiently.
More Resources:
SCSeTools Landfill Data Monitoring and Analysis
Staying Ahead of Odor Management at Solid Waste Facilities
The EPA’s published clarifications, technical revisions, and new rule versions for the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) and New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) for MSW landfills may feel like alphabet soup right now.
SCS Engineers’ upcoming webinar and open Q/A forum on July 15, 2021, at 1:30 Eastern Time is free and could help keep you informed and on track for compliance by September 27, 2021.
Our panelists will advise on the essential key information, deadlines, and changes to field operations to address during the transition from the old to the new NESHAP and NSPS rules.
• Surface emissions monitoring;
• Wellhead monitoring and corrective action requirements;
• Delegation of authority to the state, local, or tribal agencies for emission standards;
• Applicability of the General Provisions under 40 CFR 63, Subpart A to affected landfills;
• Monitoring data for control devices during startup, shutdown, and malfunctions (SSM);
• Gas collection and control system installation;
• Compliance timing and reporting;
• Open question and answer throughout the webinar.
The EPA’s published clarifications, technical revisions, and new rule versions for the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) and New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) for MSW landfills may feel like alphabet soup right now.
SCS Engineers’ upcoming webinar and open Q/A forum on July 15, 2021, at 1:30 Eastern is free and could help keep you informed and on track for compliance by September 27, 2021.
Our panelists will advise on the essential key information, deadlines, and changes to field operations to address during the transition from the old to the new NESHAP and NSPS rules.
• Surface emissions monitoring;
• Wellhead monitoring and corrective action requirements;
• Delegation of authority to the state, local, or tribal agencies for emission standards;
• Applicability of the General Provisions under 40 CFR 63, Subpart A to affected landfills;
• Monitoring data for control devices during startup, shutdown, and malfunctions (SSM);
• Gas collection and control system installation;
• Compliance timing and reporting;
• Open question and answer throughout the webinar.
When Melissa Russo’s boss Phil Carrillo told her he thought she should get her drone pilot license, she thought he was kidding. At the time, she worked on SCS’s Remote Control (RMC) team; selling drone services was a part of her job, but she had not thought of flying these unmanned vehicles herself.
Her thirst for competition kicked in when he turned the proposition into a bet. He was going after his pilot license himself; she bet she’d beat his score. They finished in a dead heat, but what started as friendly rivalry ended up bringing a new dimension to Russo’s job— a job that continues to expand in breadth as new opportunities turn up.
Today she not only flies, sells drone services, and teaches others how to sell and fly, but she’s helped bring geographical information systems (GIS) into RMC’s portfolio. How these technologies fit together is RMC remotely collects data from drones and different landfill systems. Then the GIS translates that data into maps, capturing a visual picture of how clients’ facilities’ systems are performing. The GIS piece is one of the latest chapters in the story of Russo’s evolving role (more to come on that).
Piloting is what especially gets her juices going.

“I love working with my team, supporting them in what they do. But when it comes to drones, I like the hands-on experience of flying myself more than telling other people how to do it.”
She controls these small aircraft from a device on the ground, sharply focused on her surroundings while keeping the drone in her sight at all times.
“You have to make sure there are no manned vehicles around; they have the right of way. And there’s a lot of continuous movement on landfills. You’re constantly aware of your surroundings. Is a truck coming? Am I in line with where dumping is going on?”
Flying drones takes muscle and mechanical aptitude.
The drone and case can weigh 45 pounds. And there are a lot of moving parts to assemble and calibrate.
Sometimes it’s manual work, pointing and rotating a remote controller to send a radio signal to tell the drone what to do. But more often, she pilots automated flights that she maps in advance and uploads the flight path specs into software that interfaces with the drone.
“When I’m flying drones, I can access areas where if I had boots on the ground, I couldn’t. I can go and explore just about anywhere, similar to when I dream— only it’s real,” she says.
With any task, she’s laser-focused, concentrating on one part of the picture at a time to grasp the details. She steps back and uses critical thinking, accumulated knowledge, and imagination to take on what’s before her.
The innovation process
“We’re pretty lucky with our timing; new and proven technologies are emerging quickly. I’m one of many SCSers with a deep knowledge of technology and practical experience in the solid waste industry. Together, we can make a difference because we understand the business and operational challenges very well. When I need an expert in another industry, I just reach out to a colleague. The learning process never ends, and each project helps me and my team constantly find better answers.
“My boss is more of a big-picture person; his ideas are huge and amazing. He comes to me with new ideas, and I figure out how to make them work and implement them,” Russo says.
She points to his idea to use proven GIS technology within RMC. She was already using GIS to map methane data, process topographic maps, and stockpile calculations. For instance, she integrates methane values into the GIS and overlaps them with imagery so her clients can zoom in on one well or get a large-scale view of the overall health of the gas collection system. But integrating GIS in new ways to incorporate multiple landfill systems would solve some expensive problems and, better yet, prevent even more expensive mitigation and repairs.
Expanding GIS applications to illustrate multiple landfill systems
“I know drones and how to process drone data. But now that we are expanding applications, I add more layers of landfill data, such as liquids, soil, the gas collection and control system (GCCS), SCADA, and surface emissions, to bring them into the RMC GIS platform. My colleagues are demonstrating these technologies at the SCS June Client Webinar.”
“I created a team of hand-picked SCS staff with both GIS and waste management backgrounds (and a whole lot of drive) to make the vision come to life,” she says. “That’s how we innovate, tight teams with access to nationwide expertise.”
Within six months of the project’s genesis, Russo and her team had integrated gas and liquid collection systems, other landfill systems, and asset management into the RMC GIS platform. She and her team now sell these applications nationwide.
Russo’s come a long way since joining SCS at age 21
In her mind, she grew up at the company. Before coming on board, she managed a shop in Manhattan Beach, California, while she began thinking about what to do next.
“I learned a lot about business and people. It was a stepping-stone – I discovered how to earn trust, build rapport, and sell. But in time, I decided I wanted a more professional job,” she recalls.
She went to work for a real estate company managing the SCS Engineers Long Beach office, where she would soon take an entry-level Accounts Payable position in SCS Field Services.
In time, she transitioned to the Health and Safety group, assisting in creating training material and managing truck fleets. Soon she was managing assets, among other firsts for her. By this point, she had developed enough software, accounting, and other administrative skills to step up fast.
Part of the job was keeping up with vehicle maintenance, so she often spoke with field staff. Many of them she already knew from her days working in the accounting department.
Growing with her SCS colleagues
“When I was in my first administrative roles, I supported many colleagues who were field techs or supervisors; they are project managers now. It feels as though we’ve grown up together, and we know and trust each other. We collaborate well and know that when we bring projects to each other that we will take care of each other,” Russo says.
She especially likes the RMC concept because remote control and automation enable her, her clients, and her team to work smarter, not harder because they leverage the technology to work for them.
“That means we can usually work from anywhere, giving all of us more time for family, friends, or allocating the time saved towards other needed to-dos. I’m up at five a.m. and, at times, may not finish work until nine at night. Somehow, us working women find the balance in between meetings, writing proposals, and answering emails; I have lunch with my two boys or take them to a park,” she says.
Bambi Lance, a veteran SCSer and her mother, works in the same business unit as Melissa does. “Mom’s been here for 16 years, and it’s interesting to have her perspective not only as my mom but as someone who knows SCS. She knows my department, and she knows me. She sees what I am doing and she along with management encourage me to do more and believe in myself.”
Russo reflects again on the concept of stepping-stones on the way to knowledge and maturity. I’m competitive and take on challenges, which has been a driving force in all I do today. It’s helped me take a personal inventory of how I am now versus the young Melissa,” she says.
She uses it to gauge her direction. And she uses it to connect to her staff. “I try to help them see you can turn almost any experience, into a positive. I want my team to see we are all learning and growing. They can, as I can, comfortably bring new ideas to the group and company, which often turn into new ways to help clients.”
She circles back to her decision to fly drones, explaining how it aligns with her career path from her first steps to today. “Becoming a pilot was a natural fit because it’s a new challenge. The craving to take on new tasks is how I grew from an accounting administrator to a project coordinator up to a business manager. It’s wanting to expand my knowledge, tackle new feats, and accomplish what I was not sure I could do. I like the challenge.”
The SCS Culture is Driven by Client Success
SCS Engineers periodically prepares SCS Technical Bulletins – short, clear summaries of U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) rules and plans. On May 21, 2021, the EPA published a Federal Plan to implement the new Emission Guideline (EG) rule for municipal solid waste (MSW) landfills. The Federal Plan is published under Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 62, Subpart OOO.
Read, share, download the Federal Plan for Landfill EG Rule Tech Bulletin here.
It goes without saying: landfill operators are forever working to stay on top of odors, especially when the community smells something and points to the landfill or when regulators come calling. This blog shares two odor stories: one around landfill gas and another around trash. Then it looks at what happened when an operator got a permit restriction over alleged hydrogen sulfide emissions; odor was not the problem here. It was a perceived health risk; learn how SCS proved a predictive model was off the mark.
Is Landfill Gas a Source of Community Odors? And Ensuring Compliance
Living up to landfill odor nuisance standards is tough. The underlying premise is that odors must limit peoples’ ability to enjoy life or property to create a public nuisance, but it’s a subjective call. How strong an odor is and sometimes even if it exists depends on perception, so the question becomes: when they aren’t sure what they are being measured against, how do operators comply and prove compliance?
SCS recently helped a client figure out how to accomplish this after receiving odor complaints from the community, ultimately leading to a state agency-issued violation.
“We needed to thoroughly investigate to identify and mitigate odors, then prove compliance to the state regulator. Making a strong, valid case without having a numeric standard to go by takes both creativity and a scientific approach,” says Pat Sullivan, SCS senior vice president.
Sullivan, a biologist and his team of meteorologists, air dispersion modelers, and engineers, had a good starting point. They knew landfill gas was the source of the problem. But they needed more data to get to the root of that problem, and the operator’s required surface monitoring did not tell enough of the story.
The team launched a series of studies relying on multiple investigative tools.
“When we may have to put in more gas collection components, as we did here, we want to be sure we install them exactly where they are needed. This entails going above and beyond the standard modeling with a more rigorous methodology to get a comprehensive landfill gas emissions footprint,” Sullivan says.
SCS began by bringing out a drone to reach more landfill areas than technicians on foot for better coverage. The drone can fly over slopes, areas too dangerous to walk due to constant movement of heavy equipment, and areas inaccessible because of snow and ice. As it flies, it shoots a laser, which identifies methane based on the light refraction by methane molecules—then incorporates the data into a map for a comprehensive, visual picture.
Knowing methane concentrations at specific locations is important, but determining where to be more vigilant in controlling landfill gas also requires knowing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) concentrations. Sometimes overall methane levels are within acceptable limits, but the hydrogen sulfide in it is elevated, which could be a problem, Sullivan explains.
Getting a good grasp on H2S’s potential impact is tricky, as levels can vary radically from one area of the landfill to another. Pat Sullivan, SCS senior vice president, has seen them range from 100 parts per million to as high as 100,000 at different locations.
SCS used a Jerome meter, a highly sensitive tool that precisely quantifies H2S down to low-level part per million levels. SCS took it across the landfill and then into the community in search of H2S hot spots.
At the same time that the team investigated surface emissions of H2S, they went deeper down, sampling each landfill gas extraction well for levels of this volatile sulfur compound to identify potentially problematic spots within the landfill gas system.
“For this, we used Dräger sampling tubes, a resourceful tool in that rather than sending 100 samples to the lab, we analyze them ourselves and get immediate results,” Sullivan says.
Technicians get accurate quantitative results within plus or minus about 20% and can view concentration readings out in the field. Results are recorded on field logs and entered into a database for future analysis.
SCS overlaid the methane data from the drone study with the H2S data on both surface emissions and wells to develop a roadmap to design a landfill gas system upgrade. It includes new wells and piping in focused areas and more blowers for increasing the vacuum to pull more gas.
“We saw immediate results,” Sullivan says.
“Total gas collected went up 15 to 20 percent. Complaints went down significantly, and our client has not received another violation since.”
Of course, as the landfill takes in more trash, it will generate more gas, so due diligence is ongoing.
“Problem-solving is a phased approach. You do what you determine to be most effective; evaluate; then do additional work to improve. We will continue to follow this site and fine-tune where needed to keep the system running efficiently and keep the community and regulators happy,” Sullivan says.
Taking Down Landfill Odors from Trash
New garbage on a landfill’s active face can be a source of offsite odors, but determining if the waste facility is responsible, and determining when, where, and how odors travel, takes forensic work. Landfill odor experts rely on multiple data sets and tools to understand what can be complex issues and ultimately devise the most effective odor mitigation program when necessary.
In a couple of recent scenarios in Southern California, SCS combined complaint data, meteorological data, and smoke studies to get a full picture that verified the decomposing waste was the odor source. Then staff helped nail down specific times the problem occurred and under what conditions; providing a concise window can save operators labor and other resources because they can execute proactive measures only when needed.
“We look at complaint data to learn the location, day, and time of the complaint, but these accounts are not reliable by themselves. So, we overlay this information with meteorological data to determine the wind conditions during those days and times. Weather-related data is important in vetting offsite odors because if the landfill is not upwind of the location when the complaints happen, there likely is another source,” says Pat Sullivan, SCS senior vice president.
Sullivan and his team begin their investigations in two possible ways – setting up meteorological stations at strategic areas on the landfill to capture wind-related data or capturing data from already situated stations. Then they produce wind roses from their findings, which graphically represent wind speed; how often the wind blows from certain directions; and how these two correlate. In these two scenarios, graphing wind data times during each day helped determine exactly when specific wind conditions are prevalent.
In one of the two cases, odors occurred in the summer and almost always in the morning. The data not only showed where the winds were coming from at those times, but also showed they were traveling at low to moderate speeds.
“We matched that information to complaints and confirmed that the wind conditions were indeed driving the odors,” Sullivan says, explaining the speeds were just enough to carry the odor molecules into the community but not high enough to disperse and dilute them.
“Now we have painted a picture of wind conditions that we can focus on to get more information. We are getting closer to designing a multi-tiered odor mitigation program,” he says.
The next step was a smoke study, which reveals how odors move offsite, identifying the exact pathways and movement trajectory. These details are important because to treat or disrupt odor molecules; operators need to intersect the odor plume before it leaves the site.
SCS odor experts release colored smoke at the time and location they believe odors are, based on the meteorological data. They film from a drone to get a bird’s eye view of the smoke plume as well as get a camera filming from a different angle, following the plume movement to identify its path out of the landfill. This method enables them to determine where to intersect the odors as they move through the air before leaving the site.
From this research came three recommended measures to take during unfavorable wind conditions:
One of the landfill operators now has the problem under control and has received no further violations.
The other site made many of the same changes and plans to open a second disposal area for smelly loads. This client has seen a significant reduction in complaints and violations, but it’s a work in progress. The next true test will come when Sullivan and his team reevaluate in the summer.
“We will see then if any improvements are needed and tweak the solution if needed.”
And as with our other clients, we are training operators on how to be proactive. We teach them how to identify and grade odors and how to follow set procedures. And we help them with strategy implementation,” he says.
Odor mitigation is an ongoing undertaking. The team continually assesses and quantifies emissions and potential impacts.
“We look for changes that will control odors or prevent them in the first place. And we provide clients with the know-how and support to stay ahead today and into the future. Landfills and waste volumes are growing and changing. It’s a dynamic scenario. And we continue to build on what we have proven and adjust to keep up to make more progress,” Sullivan says.
Showing That a Model Can Over Predict H2S Emissions
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) can be problematic even at very low concentrations, so this volatile sulfur compound is on federal, state, and local regulators’ radar. Some jurisdictions require the evaluation of air toxic emissions to determine potential health impacts to nearby communities.
They are also calling for these evaluations during permitting or to decide when controls are needed. To make these impact determinations, regulators typically rely on standard H2S risk assessments leveraging air dispersion modeling that predicts concentrations at locations away from the source.
However, this methodology, which includes estimates of emissions and predicts offsite concentrations based on algorithms that mimic how air moves, is not always accurate. Inaccuracy proved to be the case at one SCS client’s site. The model overpredicted offsite measurements of H2S that the state and local agency classifies as toxic.
Ultimately, the client entered into an enforcement agreement with the state because the operator had a permit limit, based on results of the risk assessment that it could not meet.
“Respectfully, the agency came in maintaining that the levels were out of compliance; it came as a surprise and seemed questionable to our team given our experience. We felt that the air modeling and risk assessment results derived from this modeling were not accurate,” says Sullivan.
First, his team tried to adjust model inputs and variables that would yield what they believed would be more accurate data. Even though they could show improvements, the model adjustments could not obtain readings that showed compliance with the risk-based limits.
Next, they began going out monthly and measuring real concentrations at receptor locations. The team used a Jerome sensor, a highly sensitive handheld device that detects H2S down to single-digit parts per billion levels with good accuracy.
When they compared the predictions from the standard model to their readings on the same days of each month and same times of day, they confirmed the concentrations were well below the acceptable risk threshold.
“Because we did this over an extended period, we have continuous readings and a large data set from many locations that give a history and statistical validity,” Sullivan says. Every monitored value was substantially lower than the values predicted by the model.
“What that means is we could show that while there were onsite emissions, they were not escaping the landfill at levels that would exceed risk-based thresholds. That was useful in proving to the regulators that the landfill was actually in compliance with the standard, even when the model suggested it was not,” Sullivan says.
Now SCS is asking for revising its client’s permit and that the limitations are made more flexible based on real-time, longer-term findings. While the team is still waiting on the final permit decision, they’re confident they have proof that the site complies with the risk-based limit.
The outcome of this project has potential beyond possibly changing one permit for one operator, Sullivan surmises.
“We think the data developed from this study showing how the models can overestimate real-world conditions can ideally help other operators build a sound case in circumstances where they truly are in compliance.”
Related Resources
Staying Ahead of Odor Management at Solid Waste Facilities – This video recording is from a live session about the challenges of odors, including measuring them and the science behind them. Throughout the recording, the speakers’ field questions as they make recommendations for assessing and avoiding odors, regulatory issues, litigation, and responding to complaints.
The presentation and Q&A run for 1 hour 41 min. It’s well worth your time, with plenty of questions posed by solid waste facility operators, landfill managers, and composting operators answered.
SCS Engineers encourages you to share this video or any from our Learning Center. You can embed them at events and use them for in-house training. Look for our
(40 CFR Part 60, Subpart OOO)
EPA is submitting a pre-publication copy of the final MSW Landfills Federal Plan to implement the Emission Guidelines (EG) and Compliance Times issued on May 10, 2021. The Final Plan becomes effective 30 days after publication in the Federal Register, impacting any remaining landfills without approved EG Cf rules.
EPA’s federal plan includes an inventory of designated facilities and an estimate of emissions from those designated facilities. The Agency estimates 1,590 landfills will potentially be covered in 42 states and the US territories of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands, and one tribal entity.
SCS Engineers is preparing a Technical Bulletin for distribution to our mailing list and on social media. The Bulletin will consolidate 133 pages into several pages highlighting significant dates and impacts for you.
Affected are MSW landfills that commenced construction on or before July 17, 2014, and have not been modified or reconstructed since July 17, 2014.
EPA is implementing emission guideline requirements for existing MSW landfills located in states and Indian country where state plans or tribal plans are not currently in effect because they were not submitted or approved.
The Final 2016 Emission Guidelines for MSW Landfills require existing landfills that reach a landfill gas emissions threshold of 34 metric tons of nonmethane organic compounds (NMOC) or more per year to install a system to collect and control landfill gas (GCCS).
It also implements the emission limits, compliance schedules, testing, monitoring, reporting and recordkeeping requirements established in the Emission Guidelines for MSW Landfills.
Unless the landfill is a legacy controlled landfill, owners or operators of MSW landfills subject to the MSW Landfills Federal Plan must submit a design capacity report within 90 days after the effective date of the Federal plan (40 CFR 62.16724(a)).
Should the design capacity report indicate a capacity equal to or greater than 2.5 million Mg and 2.5 million m3 of solid waste a landfill can accept; then, an annual NMOC emission rate report must also be submitted within 90 days after the effective date of the Federal plan, and then every 12 months until the landfill installs a GCCS (40 CFR 62.16724(c)).
You may find a copy here on EPA’s website.
Contact your SCS project manager or for assistance. Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, or Facebook to receive EPA alerts and SCS Technical Bulletins, along with other news.
SCS Engineers, a top-tier ENR environmental consulting and construction firm, welcomes Professional Engineer Mary Kennamer to its environmental services team in Raleigh, N.C. As a Senior Project Professional, Mary is responsible for designing and engineering solutions to help landfills, manufacturers, and businesses comply with federal and state environmental regulations.

As a chemical engineer, Mary’s background and degree are useful to help North Carolina landfill owners prepare to meet more stringent federal and local air regulations. She will advise on air compliance issues, air permitting, compliance reporting, and consulting for landfills and manufacturing.
“Mary’s previous consulting experience and work with the US EPA is a tremendous asset and value for our landfill and manufacturing clients,” states Kenton Yang, the Raleigh office’s project director. “We’re excited to add another bright star to the Raleigh office.”
In order to permit new or expanding plants and facilities, there are complex environmental policies to meet. As an environmental and chemical engineer, Mary researches, plans, and completes the technical work for air permitting and compliance, SPCC, and due diligence that keeps owners in compliance and projects moving forward.
About SCS Engineers
SCS Engineers’ environmental solutions and technology directly result from our experience and dedication to solid waste management and other industries responsible for safeguarding the environment. For more information about SCS, please visit our website at www.scsengineers.com/, contact , follow us on your preferred social media, or watch our 50th Anniversary video.
SCS Engineers – Raleigh specializes in permitting and meeting comprehensive clean air, water, and soil goals and provides a range of services such as PFAS treatment, solid waste master planning, landfill technology, risk management, groundwater monitoring, pre-closure and landfill closures, and Brownfields remediation.
When Doug Doerr got a call from a Colorado-based landfill operator with a hot gas probe at his site’s boundary, Doerr’s day kicked into high gear. Chasing down gas migration problems is nothing new in an SCS client manager’s life, but that reality makes the job no less complex. And in this scenario, he was dealing with a site that he occasionally got called to visit, so to understand the problem fast, he needed the site’s historical data and the current information to fully picture what was happening.
Doerr started with basic landfill gas information from the client: the monitoring probe’s location and a drawing of the gas collection system to determine where the probe was in relation to the gas system. But as you know, that is one small slice of a king-sized pie.

“I queried our in-house landfill gas technical group (engineers, geotechnical experts, and field personnel). And got over 25 responses within several hours with suggestions, one of which came from Ken Brynda in SCS Field Services, who leveraged DataServices to help me identify and narrow down the potential cause of the problem,” recalls Doerr.
DataServices, a module of the SCS eTools® digital platform, collects, stores, manages and analyzes large volumes of continuously accumulating landfill gas data for individual sites or multiple landfills. The module provides a quick method to view landfill gas scenarios.
The beauty of it is that it generates maps and charts to visualize every well and every probe. These system components are viewed in relation to one another and in relation to the perimeter, where the methane on that Colorado site flowed. Further, SCS Field Services’ landfill gas gurus, such as Ken Brynda, plug-in specific parameters that keep a close watch on any well or a group of wells.

As responders viewed initial results from their respective bases around the country, Brynda churned out more information in a few hours, running point charts to capture the balance gas, methane, flow, temperature, supply vacuum, and the vacuum applied to each well. He looked for trends that narrow down cause and point to solutions.
Eliminating the Possibilities – Rule Out Well System Malfunctions
“It can take days if we’d had to do it the old school way with spreadsheets laid out in a lot of rows. But we could identify the potential problem in a matter of hours, backed by a comprehensive evaluation for the landfill operator in eight hours,” Doerr says.
When Field Services staff work to solve a problem with a probe, they look for an outlier, something from a group of wells that’s not behaving like the other wells. In this case, Brynda determined that the wells near the hot probe were functioning properly. DataServices eliminated potential problems by slicing through and analyzing large chunks of data confirming the system was working efficiently.
Next, we observed that the wells are likely too far away to pull gas back from waste, adjacent to the probe in question, where there are no wells.
“DataServices helped rule out malfunctions, and that’s a big deal because if you can confirm the landfill system is working properly, you have narrowed your focus and can look toward other possibilities, ultimately leading to corrective options,” Doerr says. Brynda and Doerr suggested putting in temporary wells in that area to avoid odor migration and health and safety issues.
Doerr continues watching the situation and is prepared with a several-point action plan to mitigate exceedances and avoid falling out of compliance. “We continue watching the data to ensure the gas collection system continues to function well. Should there be issues again, we’re able to fully identify the gas migration pathways and anything in the system that looks out of the ordinary,” Doerr says.
If the client decides to add wells in time, data from the expanded infrastructure will be added to the app and monitored. “As the number of wells grows, DataServices grows with it, adding any, and as much, monitoring and collection data as the operator wants. DataServices will always be in the background to monitor, collect and analyze LFG data in real-time, whenever we need it,” he says. Being able to store, organize, dissect and analyze unlimited volumes of information from one location is powerful. And not just because it helps operators identify problems as they are happening, but because it and our teams can support them in looking for trends over time. Keeping an eye on the activities that keep the systems in balance is less costly.
For Doerr, who spends time in the field but longer hours with his clients, DataServices and the ability to interact quickly with experts like Brynda help SCS deliver more value to clients. “As much as I’d love to master DataServices, I need to focus all of my time on my clients’ business and goals; having support from Field Services and DataServices makes us all more efficient.”
Landfill Technologies and Comprehensive Expertise
SCS eTools® and SCS DataServices®, now with SCS MobileTools® for viewing data and charts anywhere; available to pull landfill data into DataServices for analyzing. You can customize and focus on exactly what you need fast. As Doug and Ken emphasize, it’s info that you likely already have, but may not be able to use quickly for troubleshooting.
SCS RMC®, remote monitoring and control of landfill equipment and systems.
Comprehensive Landfill Services