

An SCS Engineers Technical Bulletin will be released early in the week.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency issued limits on methane emissions from oil and gas wells that are more stringent than those it proposed last year. The final regulations released on Thursday, May 12, 2016, will add hundreds of millions in additional costs per year; at least 25 percent higher than the preliminary version published in August 2015.
EPA Administrator Gina McCarthy told reporters on a conference call that the mandates, applying immediately to new and modified wells, are a “critical first step in tackling methane emissions from existing oil and gas sources.”
Under the rule, companies must upgrade pumps and compressors while expanding the use of “green completion” technology meant to capture the surge of gas that can spring out of newly fracked wells. Such green completion techniques have been required for new and modified natural gas wells since 2015, but Thursday’s rule would broaden the requirement to oil wells too.
Take me to the EPA summaries. Click on the information sheets listed below:
“Our clients enable SCS to build, grow, and sustain an engineering firm dedicated to solving environmental challenges,” said Jim Walsh, President and CEO of SCS. “We sincerely thank our friends, colleagues and, in particular, our clients for helping us achieve a highly regarded ranking each year.”
Firms are ranked in terms of revenue by Engineering News-Record magazine (ENR), as reported in the May 2, 2016, issue of the “ENR Top 500 Design Firms Sourcebook.” SCS has made the Top 500 list since its publication in 2002 and has ranked in the top 100 of that list since 2008.
When sorted by firm type, SCS Engineers is ranked the second largest environmental engineering firm (ENV) and is ranked in the “Top 20 Sewerage and Solid Waste” service firms in the nation. SCS has made this top 20 list since 2002.
Later in the year, ENR will publish additional resources and lists, including the “Top 200 Environmental Firms” issue, typically published in the month of August.
Learn more about our latest innovation, SCSeTools
Penton’s Waste360 Unveils the Next Generation of Leaders in the Waste and Recycling Space Award

The Waste360 “40 Under 40” awards program recognizes inspiring and innovative professionals under the age of 40 whose work in the waste, recycling, and organics industry has made a significant contribution to the industry. Dave Hostetter focuses on designing landfill gas systems and landfill gas flare systems. Although still considered a young professional himself, he serves as a mentor to other engineers, providing guidance with hands-on design as well as professional guidance.
Dave is a LEED® Accredited Professional (LEED AP) and a Certified Energy Manager (CEM). He brings to SCS Engineers an abundance of expertise and fresh ideas. Dave has a keen eye for troubleshooting and diagnosing control system issues. He serves SCS clients wholeheartedly and goes out of his way to provide assistance as well as the expertise needed to make their day-to-day operations run as smoothly as possible. Dave has participated in a multitude of landfill gas and leachate system designs, including designs for blower and flare stations, wellfields, gas conveyance piping, leachate pumping systems, and groundwater extraction systems. His vast and varying experience, honest and hard-working approach to projects, and his positive attitude make him a respected resource within the firm.
Dave lives the SCS mission, and clients trust him for his honest and comprehensive approach to their challenges. Dave takes ownership of his work and puts in the time and effort to deliver excellent results and maintain a great relationship with his clients. “Dave Hostetter sets the example of how an honorable, dynamic, and experienced engineer should act at SCS,” said Paul Mandeville, Senior Vice President and Director of SCS’s offices on the east coast. “Dave serves as a model of what young professionals and students should strive to become in their professional and personal careers; we are very proud of him.”
Please join SCS in congratulating Dave Hostetter on his recent recognition by Waste360.
If you are buying or selling a property with a history of soil or groundwater contamination in Wisconsin, the state’s Department of Natural Resources requires vapor intrusion pathway screening. The screening is also necessary when buying or selling a property adjacent to a property with soil or groundwater contamination. Is this analysis necessary?
The screening is essential; vapors from contaminated soil or groundwater may transfer to indoor air, causing health risks. The vapors may or may not have an odor. Screen testing and analysis will determine their existence and the level of concentration. Most commonly levels are low, and no additional action is necessary. If beyond the threshold determined safe by your state, some mitigation may be required before purchase.
It is not a simple matter to apply an individual state’s current regulatory guidance to determine the need for vapor intrusion mitigation. The actual intrusion, or expected intrusion in the case of new buildings, is often overstated, and some regulatory agencies use screening values for indoor air chemical concentrations that are at or below levels commonly found in buildings. The slightest error in sampling technique can dramatically affect the resulting data.
SCS offers the full array of vapor intrusion services for residential, commercial, and industrial properties, and for developers, municipalities, lenders, attorneys, industrial facilities, tenants, landlords, and buyers and sellers of real property.
Contact SCS at 1-800-767-4727 or email us at .
Question about this blog, please email one of the authors Robert Langdon and Thomas Karwoski.
SCS has offices nationwide to serve our customers. To learn more about vapor mitigation, please visit the SCS website here: https://www.scsengineers.com/services/hazardous-waste-and-superfund/vapor-intrusion-mitigation-systems.
The Solid Waste Association of North America (SWANA) Applied Research Foundation released a report concluding that: a significant amount of additional food waste processing capacity will be required to achieve national, state, provincial, and local food waste diversion goals. The report also emphasizes the need for local decision-making in selecting and implementing those food waste diversion programs.
…a significant amount of additional food waste processing capacity will be required to achieve national, state, provincial, and local food waste diversion goals. The report also emphasizes the need for local decision-making in selecting and implementing those food waste diversion programs.
The report goes on to say that interest in recovering food waste from municipal solid waste is growing to meet goals established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Agriculture, but many major metropolitan areas lack the infrastructure to manage the ability to meet the established goals. Two examples were cited:
Several states, including Massachusetts and Connecticut, condition their food waste diversion requirements on the ability of generators to access adequate capacity within a certain distance.
Speaking as SWANA’s Executive Director and CEO David Biderman stated:
We believe that Americans need to rethink how food is handled before it is considered waste, to divert it into programs to feed people, and to find other productive uses for food as food. Once it becomes waste, however, municipal decision-makers, working with their processing partners, need to determine how to best manage the material.
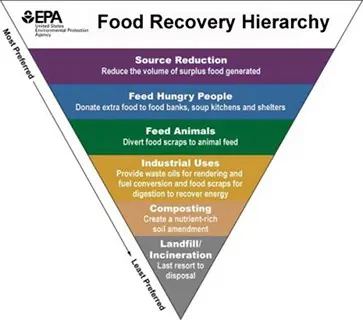
The SWANA report focuses on the effects of food recovery at the two lowest tiers of the hierarchy – composting and landfilling/incineration. The report concludes that food waste diverted from landfill operations has the potential to be processed at composting facilities. Then, going on to say that anaerobic digestion (AD) and co-digestion at wastewater treatment facilities are also likely destinations for diverted food waste.
Jeremy O’Brien, Director of the Applied Research Foundation, noted:
The food recovery hierarchy does not apply universally; an analysis of greenhouse gas impacts based on local data and conditions is needed to identify the best food scraps management options for a specific community.
The report encourages solid waste managers to perform a life cycle analysis of economic and environmental costs and benefits based on local needs, system capabilities, and data to identify the most effective ways to manage food waste at the local level.
SCS Engineers and SWANA are both long-time advocates for local decision-making in establishing programs to collect and manage municipal solid waste.
Related articles:
Infrastructure Week (May 16–23) is a national week of events, media coverage, education, and advocacy efforts to bring the state of the nation’s infrastructure to the attention of all Americans. Forester Media, the publisher of MSW Management magazine, is an Infrastructure Week affiliate. John Trotti, MSW Managing Editor recently surveyed Jim Walsh, P.E., BCEE, President and CEO of SCS Engineers and long-time friend of the magazine on the topic. Jim is first out of the blocks to answer the four questions John asked of respondents from MSW and Forester’s other publications, Business Energy, Erosion Control, Grading & Excavation Contractor, Stormwater, and Water Efficiency.
MSW Management (MSW): Which infrastructure projects should be given priority? Roads and bridges? Dams and levees? Water supply? Electrical grid? Waste management?
James Walsh (JW): Typically public safety, cost, and benefit determine the priority for infrastructure projects, and different political jurisdictions have different priorities. Where highways and bridges are new but waste management facilities are old, the priority might be waste management facilities, and vice-versa. Some types of infrastructure are more amenable to private sector solutions, which can allow the government to focus on other types of infrastructure. The trend in waste management, for example, has been to rely on the private sector in the last decade
Each segment faces difficult challenges; the most significant is funding. Waste management does not necessarily have priority over other projects, but has progressed by regionally identifying the infrastructure necessary. Thus, each region avoids the pitfalls of competing for funding with other regions and other projects.
SCS Engineers focuses on waste management, but there are opportunities to interact with other segments in sustainable ways. For instance, we have energy clients who supply coal ash to specialty cement companies who use it to make “green” cements that last longer in applications such as road construction. We design and construct facilities that take the byproduct gases from the decomposition in landfills to generate electricity reducing their dependence on fossil fuels, or directly use the gas for energy to power wastewater plants simultaneously cleaning and conserving water. We find ways to safely redevelop contaminated property supported by existing infrastructure, thus reducing the need to build new infrastructure.
In short, we work toward helping clients find sustainable solutions to infrastructure projects.
MSW: Is there a solution to long-term infrastructure funding?
JW: With respect to the waste management infrastructure, waste systems require significant capital investment in land, equipment, facilities, and infrastructure. While many governments have decided to rely on private industry instead of financing new governmental facilities, others have become much more sophisticated in adopting private sector approaches to financing. Pro-Forma Economic Life-Cycle Models can assist governmental entities to identify the critical variables that can impact the success of an infrastructure project. Moreover, economic models evaluate how various components of a waste system and variable assumptions integrate together into a sensible approach. Pro Forma Economic Models allow for a careful analysis of the life-cycle costs and potential revenue sources and identify factors that will influence the waste system costs and demonstrate how to adequately and equitably fund the system. These Models provide different scenarios and eliminate options that are not financially feasible or do not fit a region’s short- and long-term needs or priorities. Sensitivity analysis can be conducted to understand better the impact these variables have on capital costs, operating expense, and the overall system economics. By assessing the economic and regional benefits first, we can focus on designing and building infrastructure solutions that are safer, longer lasting, and affordable. Other benefits include adjusting the Model if there is a major change in the commodity market, such as plastics’ recycling is experiencing now and when considering the use of new technologies.
Every industry segment and every region have a different blend of socio-political conditions, geography, and monetary resources—we assess and design to their particular needs. Adopting new waste management technologies, such as anaerobic digestion or waste diversion, as part of an overall waste management program can be integrated into the Model to study how, and if, they sensibly integrate within the existing program. New technologies are typically more expensive than mature technologies such as recycling facilities and landfills, but that condition alone is not why they are considered valuable to a region. The framework considers elements key to integrating anaerobic digestion for example into a long-term program. Capital investment, a significant centralized source of high-quality organic waste, power costs and economic utility incentives, limited land suitable for composting, lack of conventional waste-to-energy facilities, or a ban on organics disposal in landfills are some of the considerations.
Many states are developing organics diversion initiatives, discouraging or banning organics from landfills; they will want to develop separate capacity for diversion within their overall program to build a sustainable plan for the long-term. In some states there is plenty of environmentally sound landfill capacity, recycling facilities have adequate capacity, and the socio-political climate has different ideals. What works in Iowa might not be suitable for California.
MSW: What kind of harm is the current state of our infrastructure doing to the economy and the community?
JW: Every four years, the American Society of Civil Engineers releases a “Report Card for America’s Infrastructure” depicting our nation’s infrastructure condition and performance. In a traditional school report card format, individual infrastructure segments are assigned letter grades—solid waste has the highest grade of B- in the most recent report published in 2013. The waste management infrastructure in the United States is robust, diverse, and significantly supports our economy and communities by providing safe and cost-effective management of the materials that we discard on a daily basis.
MSW: What can various government entities—from local to Federal—do to attract private sector support and investment?
JW: In the United States, private solid waste facilities manage 75% of the municipal wastestream. The waste management industry has many examples of public/private partnerships and significant investment by the private sector. Just look at firms like Waste Management Inc., Republic Services Inc., Waste Industries, Waste Connections, WCA Waste Corporation, Covanta, and Wheelabrator, which own and operate numerous landfills, compost facilities, waste-to-energy facilities, transfer stations, processing facilities, alternative technologies, and hauling companies. These facilities require significant private investment. Allowing private industry to participate in the management of waste management infrastructure brings needed fiscal discipline and accountability to the overall waste system infrastructure.
The private sector is attracted to markets that are predictable and that provide an appropriate return on investment. Jurisdictions with a reputation for making sudden unpredicted changes in regulations that adversely affect the return on investment will find it difficult or impossible to attract private sector support.
The waste management sector and SCS Engineers have seen our share of magic technologies that are literally too-good-to-be-true, yet somehow attract governmental support both financial and otherwise. It is fine for government agencies to provide grant support for research related to promising new technologies, but adopting an unproven technology as the sole means of waste management is inviting a public health crisis. Private sector investment is not attracted to jurisdictions that have unrealistic expectations.
About James Walsh, PE, BCEE, President and CEO of SCS Engineers

Jim has worked at the forefront of sustainable waste management for more than 40 years. He has authored numerous publications, technical support documents, presentations for the USEPA, US DOE, the Gas Research Institute while serving the Solid Waste Association of North America (SWANA), National Waste and Recycling Association (NWRA), and the Environmental Research and Education Foundation (EREF), among others.

Long story short, an escapee from San Quentin and any uncontrolled methane air molecule may be more similar than we may presume. In fact, a common LDAR practice is to use an infrared imaging camera; similar to the camera often used in search of fugitive criminals.
On a serious note, fugitive emissions are something that both industry and regulators have been focused on for decades, and the past and present efforts made to limit them are no less than remarkable.
Specific to Onshore Oil and Gas Exploration & Production, the Federal Regulations applicable to fugitive emissions are fairly young. Finalized in 2012, NSPS OOOO is no longer a toddler and is in the middle of growing into NSPS OOOOa (Public Comment Deadline March 11, 2016). On a national scale, NSPS OOOOa will expand fugitive emission monitoring and control requirements (VOC’s and methane) to several facility types associated with the industry and is expected to be finalized before the close of 2016.
In California, fugitive emissions from Onshore Oil and Gas Exploration & Production have been regulated for a long time. In fact, the O&G industry in Santa Barbara County has dealt with fugitive emission requirements since 1979. Since then SCS Engineers has been assisting with fugitive emission monitoring for our valued clients. Today, SCS Engineers provides the Oil and Gas Exploration and Production industry with efficient and effective LDAR services.
So fear not, SCS Engineers is ready to supply the knowledge and skill set you need to stay compliant, maintain your operations, and respect your bottom line. Remember, unless the doors are closed, pumps are turned off, and equipment is flushed and plugged; fugitive emissions requirements and LDAR will likely still apply.
Applicability: Determining Federal vs. State oversight is the first step. Non-Major Source Oil and Gas Production facilities are either subject to NSPS OOOO (soon to be OOOOa) or a related State specific rule (i.e. Colorado Regulation 7). Once oversight is determined, then there may still be exemptions for your facility (i.e. facility constructed before August 23, 2011). And finally, once regulatory oversight is confirmed and you determine that LDAR is required for your facility, then the last step is to figure out which equipment is applicable (i.e. VOC content > 10% by weight). Basically, an applicability determination can be daunting.
Equipment: EPA’s Method 21 is historically and currently referenced in all LDAR regulations. Method 21 requires an instrument such as the Flame Ionization Detector (FID) or Photo Ionization Detector (PID). More recently the Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) Camera has been included in LDAR regulations and utilized in LDAR programs. Presently, there are several instrument technologies that exist and are in the works, but not yet mainstream in Oil and Gas sector. Ultimately, if you were to find yourself conducting LDAR monitoring at your oil and gas facility tomorrow per an established regulation, you would most likely need to use an FID or OGI.
Recordkeeping: Personally, I like the simplicity of using paper forms for field notes; however, the old-fashioned way comes with risk. The up-front and ongoing data involved with an LDAR program is too much for maintaining a paper to computer process, regardless of how organized you think you are. Therefore, a computer database platform is recommended and necessary for managing your LDAR recordkeeping. Beyond just recordkeeping, a database platform can organize schedules, alerts, generate reports, extract trends, and many other applications to help keep your LDAR program compliant. One such platform worth considering is SCSeTools™. This cloud-based software can provide the database capabilities used on the desktop, but almost more importantly, provides mobile data input capabilities with the SCS MobileTools™ application fit for Android and IOS systems. Keep the fugitives from escaping, and document containment for the authorities!

Whether you want to discuss LDAR or Dodger baseball, don’t hesitate to contact me, or SCS Engineers.
Resources:
Learn more on the SCS service pages and read SCS project case studies from across the nation to help fine tune your program.
Outside links to the EPA proposed rulemaking website:
This workshop was insightful, tightly constructed, and – most impressive – able to deliver high quality information that businesses can use immediately. I have been to hundreds of business workshops where companies feel drowned in the amount of expert information coming at them. Not so at this concise, one-hour workshop where businesses clearly understood the next steps they should take and where they can find resources to help them proceed.
Jo Marie Diamond, President and CEO, East County Economic Development Authority after attending the SCS seminar in San Diego, CA. on March 1, 2016.
SCS Engineers staff professionals are available to answer questions about compliance and the proposed fee schedule changes for attendees and any business unsure about the storm water permit. We can help clarify questions such as:
See the slide presentation here if you have not attended the seminars.
If you have questions about how the storm water permit could impact your business, or would like to know more about the permit fees, please contact Cory Jones, your nearest SCS office in California, or .
Cory Jones, P.E., ToR, QSIP, is a stormwater program manager at SCS Engineers. Jones manages complex projects for private and public clients that include site/civil, water/wastewater and stormwater engineering. He has completed a wide variety of special studies in storm water management and National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) compliance for federal, state and municipal public agencies.
Thirty-four senators and 171 representatives argue in a brief filed February 23, that the EPA overstepped its boundaries in creating the carbon-cutting Clean Power Plan. In short, the brief states that they feel that Congress never gave the EPA a clear statutory directive or authority to transform the nation’s electricity sector. The brief points out that the EPA seeks to make “decisions of vast economic and political significance” under a “long-extant statute,” and in doing so must point to a “clear statement from Congress.”
Yesterday’s brief comes just two weeks after the U.S. Supreme Court ruled the EPA cannot begin enforcing the rule until legal challenges filed by 25 states and four state agencies are resolved.
The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals will hear oral arguments on the merits of the states’ case on June 2.
With the brief it is clear that the Clean Power Plan is not only facing legal challenges but also political ones. It may be left for the next Administration to pick up this pieces and decide the fate of the Plan.
SCS Engineers ranks 4th on the Los Angeles Business Journal’s list of the top 25 largest environmental services firms in the Los Angeles region. “We’re very proud of our environmental work in California and across the nation,“ stated Pat Sullivan, BCES, CPP, REPA, and a Senior Vice President of SCS Engineers. “It’s especially rewarding to know that we make a positive difference in our backyard and for the regional economy.”
See the Los Angeles Business Journal List