

Sam’s contributions help the waste industry reduce environmental and health risks. His work improves the quality of life for workers in the industry and the communities surrounding our waste facilities.
Sam develops remote monitoring and control (RMC) SCADA systems that meet environmental management needs at landfills and industrial facilities. Operators can monitor and control their landfill equipment (e.g., flares, blowers, pumps, tanks, etc.) from anywhere using their phone or computer.
During COVID, he implemented RMC systems enabling operators to continue running essential services safely without physically traveling to the facility, and are especially valuable when facing labor shortages.
SCS is proud of our five candidates submitted for consideration this year. We’ve never submitted so many before; it’s a wonderful indicator of the talented professionals working at SCS, where company ownership spurs creativity and leaders. See our previous winners here.
In 2006, a Northeast Ohio landfill discovered a curious and concerning occurrence – temperatures rising inside the waste mound. In addition, the same development was found over the next several years at several more sites. At first, there was concern that the elevated temperatures were due to overdrawn gas extraction wells causing oxidation and fires in the waste. But soon, it was determined that the elevated temperatures were deep in the waste where anaerobic conditions with no atmospheric air intrusion, oxidation, or fire were possible, essentially debunking the landfill fire theory in those cases. These occurrences were a new anaerobic condition in the waste, beyond the typical methanogenic (or methane generating) reactions typically found in mature landfills.
Once it developed at similar sites, landfill experts began referring to the reaction status and affected landfill condition as an “elevated temperature landfill” or ETLF. Now, the industry identifies several common conditions in roughly 20 of them – some with gas and in-situ waste temperatures of 180 °F and higher (100 to 120 °F is normal).

Knowns and unknowns,
Why every operator of a sizable landfill should look out for rising temperatures,
What to do should they see a problem, and
The focuses of current research as more sites are under watch.
“When we first started seeing elevated temperatures, everyone thought it was another fire, and though we have learned a lot in 15 years, it’s not always easy to distinguish between an ETLF and fire. But we do know that, often, overdrawn gas extraction wells that pull oxygen from the atmosphere into the waste mass can create landfill fires,” Walsh says.
“We’ve known for decades that air intrusion causing aerobic activity inside a landfill can create and fuel landfill fires. But many of my peers and I became convinced that a new type of anaerobic reaction was causing rising temperatures,” he says. They were leaning in this direction because they know that an indication a fire may ensue or exist is if there’s more than 5% oxygen or 20% nitrogen in the gas drawn into a landfill gas extraction well. But in ETLF’s we did not see any evidence of elevated oxygen or nitrogen. Something else was happening, causing the sites to heat up to 180 degrees F or more.
The team delved into operators’ landfill databases, discovering three trends at least six months and sometimes years before temperatures rise:
Gas composition, which is typically 50% methane (CH4) and 50% carbon dioxide (CO2), began to change. The CH4 level drops, replaced mostly by CO2.
They learned that the pH of leachate moves from slightly alkaline to acidic (dropping to 6 and lower). The third condition they found is that hydrogen creeps up to between 1% and 15% of the landfill gas composition.
“But you have to look analytically at all the puzzle pieces. Rising CO2 and dropping CH4 can signify either a landfill fire or ETLF. Suppose you have this change in gas composition coupled with elevating hydrogen levels of 5% to 15% or more, lowering pH levels, elevated temperatures of 180 degrees, and the absence of smoke or steam. In that case, you likely have an ETLF,” Walsh advises.
The underlying cause and conditions driving an ETLF are still not well understood. Accurately assessing, quantifying, and modeling thousands of different reactions in landfills and the heterogeneity of the in-situ waste has made it difficult.
Even harder than understanding ETLF reactions and predicting the conditions that drive them is knowing how to prevent an ETLF, extinguish it once it develops, or stop it from expanding.
What could be the root cause?
The first known site in Ohio received a lot of aluminum production waste (APW) — mostly production residuals and air pollution dust removed by air pollution devices. That seemed to be the root cause of that ETLF condition at that landfill, and the hope was that ETLFs might be limited to landfills that receive APW. But in the years immediately thereafter, ETLFs developed at two other sites – one in Southwest Ohio in 2009 and another in Missouri in 2011. Those two sites had no known APW and no known material quantities of other special waste that might trigger their ETLF conditions.
Look to deep, wet landfills.
“We looked through waste receipts carefully and couldn’t put a finger on a specific special waste material as a cause. But we did learn that there’s more potential for ETLFs to develop in deep, wet landfills,” Walsh says.
The problem is that practically every site east of the Mississippi is wet, and most landfills active today are both deep and large – deeper and larger than the average landfill of the past.
“So, I think that almost every active municipal solid waste (MSW) landfill has to look at the gas and leachate data very carefully to determine if they have a developing elevated temperature landfill,” he says. That’s not to suggest that a majority of such landfills become ETLF’s. In fact, ETLF’s are rare and in the minority of all landfills today. It’s just that there may be some risk of ETLF conditions developing at such sites, and it’s worth keeping an eye on those characteristic conditions over time.
It is especially challenging for the industry to know what to do once they confirm an ETLF is developing.
There’s been a lot of discussion on how to stop the reaction. Several aggressive technologies, including very cold CO2 and nitrogen (N2) injection into the waste to cool it and hopefully extinguish, or at least stop the growth of an ETLF reaction, have been done at a few sites. But applying these cold gases homogeneously throughout the targeted waste volume is quite challenging, if not impossible, so that some aggravating conditions will likely continue and may go on to spread further.
“The usual best and most effective course is to monitor, contain, and manage elevated temperatures carefully. We’ve found that as our best recourse,” Walsh says.

Your gas extraction system is key.
While operators should throttle down or shut off gas extraction selected wells in affected areas with landfill fires, with an ETLF, it’s critical to continue drawing gas at the rate it’s generated to mitigate the buildup of heat and pressure in the waste mass.
Rather than use plastic pipes, operators may need to use temperature-resistant gas well materials that won’t melt or otherwise fail. And they must consider that with added stress on the gas collection system, wells can fill with liquid.
So, Walsh advises, drain gas wells of liquids promptly and as completely as possible. Doing so removes heat buildup in the liquids and opens up more of the gas well column to extract higher gas volumes and lower gas pressures in-situ in the landfill. Adding additional wells between existing locations can also facilitate the extraction of more gas and liquid to reduce further gas pressure and heat that is otherwise trapped and held in the waste.
Maintaining secure, tight landfill covers is equally important, as elevated temperatures can lead to rapid settlement, with resulting cracks and fissures in the cover, allowing fugitive gas emissions.
The elevated heat levels accelerate waste decomposition, reducing in-situ waste volumes and, with that, causing rapid differential settlement at the surface. Such rapid settlement amplifies stress on landfill infrastructure and can cause cracks and fissures and ultimately fugitive emissions and odors. Some operators find the best approach is to move to a very airtight surface cover such as an exposed geomembrane cover (EGC) to contain emissions, preventing gas from venting between extraction wells. These covers have the added benefit of enhancing gas collection volumes.
Leachate collection infrastructure should not be affected, at least if it’s at the bottom of the landfill.
The reaction is typically at the center, vertically, and does not travel to the bottom of a landfill. However, ETLFs can generate significantly more liquids, both leachate and condensate. And contaminant levels in these liquids may be higher, creating challenges in treatment and disposal, Walsh advises.
Consequently, some of the few operators battling elevated temperatures, with larger volumes and harder-to-treat liquids, may lose access to their local wastewater treatment plants and be forced to go elsewhere, hauling hundreds of miles in some cases. Leachate hauling and treatment costs may be significantly higher.
Research is ongoing, with The Environmental Research Education Foundation (EREF) at the forefront.
One goal of landfill engineers and scientists is to figure out the underlying causation and reaction, which has proven a big challenge due mainly to the thousands of reactions and heterogeneity of waste that Walsh discussed earlier.
EREF studies have models to try and determine if a landfill has a high potential for ETLF conditions to develop. Still, it’s been difficult to model the likelihood an ETLF condition will develop with any degree of certainty so far. Special wastes may be a factor, including aluminum production waste (as previously mentioned). Ash and biosolids may also be issues when receiving them at a landfill in significant quantities relative to conventional MSW.
An ongoing focus of EREF studies is now looking at how to place special wastes within the landfill in a manner that ETLF conditions are less likely to develop. That includes allowable quantities of such special waste relative to total waste volumes and how such special wastes are mixed with the general waste stream received, and in turn, how they are positioned within the landfill geometry. In many cases, it may be advisable to isolate such special wastes in monocells, separate from and well isolated from the general waste stream.
Monitor, then contain and manage.
“We’ve learned a lot about ETLFs over time. But while we know some special wastes that release heat seem to have higher potential, I don’t think we will be able to nail down precisely what triggers the reaction. Or, exactly precisely what landfill with what conditions will become elevated temperature landfills,” Walsh says.
“We have to watch precursors and developing conditions to see if the trend is to move along that continuum of elevated landfill temperature and other indicators like gas composition and leachate pH. Then your best recourse, again, is to preemptively and aggressively contain and manage.”
Additional Reading and Resources:
Prevent, Identify, and Mitigate ETLF Conditions
ETLF Conditions – Best Management Practices
Videos:
Monitoring Tools: SCS DataServices and SCS RMC
Questions and Comments: Contact us at
If you thrive in a friendly, collaborative, and client-focused company, SCS Engineers is the place for you. We’re looking for field technicians to work collaboratively on our Field Services teams nationwide. Use our job search to find your desired location. Specific information is posted for each open position.
Under general supervision, our technicians operate, monitor, and maintain gas migration control and recovery systems, including gas well monitoring and adjustment, troubleshooting, and system repairs. Be part of a team working for the good of our clients, communities, and the environment.
Charles Hostetler, Ph.D., and Kacey Garber join the award-winning SCS Engineers practice serving the region.
As more businesses and municipalities move toward sustainable practices to help protect natural resources, the environmental consulting and contracting firm SCS Engineers is experiencing exponential growth. Most recently, SCS welcomes two professional staff in Peoria, Illinois, with impressive groundwater and wetlands protection backgrounds.
Landfills are required to monitor the underlying groundwater for contamination during their active life and post-closure care period. They operate using modern engineering methods, liquids management systems, and technologies that meet or exceed state and federal compliance. Landfill development may impact existing wetlands or navigable waters of the United States; developing new water resources mitigates or offsets those impacts.
Dr. Charles Hostetler has over two decades of experience as a hydrogeologist planning and overseeing groundwater and wetlands protection programs. His field experience helps solid waste facilities site and run operations safely while proactively monitoring and protecting groundwater and wetland resources. His diverse experience includes developing conceptual designs for the treatment of PFAS in liquid waste streams and sequestration in landfills. You can learn more about Charles Hostetler here.
Ms. Kacey Garber comes to SCS as an experienced hydrogeologist specializing in solid waste management permitting and groundwater monitoring well design and construction projects. Her areas of expertise include groundwater and wetlands monitoring, environmental sampling, hydrogeological site characterizations, groundwater monitoring well design, monitoring well installation oversight, and designing special groundwater studies. You can learn more about Kacey Garber here.
SCS Engineers Business Unit Director Eric Nelson says,
Charles Hostetler, Ph.D., and Kacey Garber bring their landfill permitting and groundwater management expertise to our environmental practice in Illinois. Charles and Kacey share their expertise on the emerging PFAS regulations applied to landfills with our industry at SWANA and NWRA conferences. Garber brings hard-rock geology and groundwater expertise. Her project leadership has been instrumental in removing a Part 807 facility from Post-Closure Care requirements. Hostetler has the distinction of having removed the only Part 811 facility from a Post-Closure Case.
…and your new colleagues say WELCOME TO SCS!
“The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, signed into law last month, will dedicate more than $1.5 billion to the U.S. EPA Brownfields program. The Act includes hundreds of millions of dollars allocated to Multipurpose Grants, Assessment Grants, Cleanup Grants, Revolving Loan Fund Grants, and technical assistance intended to improve equity, create jobs, and mitigate environmental degradation.”
CCLR has provided the expected breakdown and timelines from EPA. The EPA has hundreds of millions of dollars allocated for FY22 that will be applied for in July and awarded in November 2022. This timeline is different and with much larger individual grants possible, up to $10mil per grant.
SCS Engineers has a stellar win rate for brownfields grant writing and implementing brownfields programs. Please let our brownfields and remediation experts know if you have any questions or if we can provide assistance in grant support.
Click here to learn more and obtain support and funding for your community’s brownfields project.
These days you see companies bending over backward to attract new hires. Puffy job descriptions, promises of success, big salaries, and benefits are everywhere. My advice is to learn about a company’s leaders — not yet retiring and not a young professional. What they talk about during interviews is often a good indication of what they are like and what they value. It has always helped guide me to work somewhere rewarding under the tutelage of remarkable people.
Mike McLaughlin is the Senior Vice President of Environmental Services for SCS Engineers and was once an SCS young professional. He graduated from law school in 1979 and continues to influence people and businesses every day, including many at SCS Engineers.
He is an environmental engineer with a law degree, and you’d be hard-pressed to find a more knowledgeable person in the field. You’d also be lucky to know him. He is as entertaining as thoughtful about finding practical solutions to environmental challenges and the things that matter.
Just reading the article A Special Place to Study Law makes me happy knowing I get to work with people like Mike, and you could too.
With great pleasure, we announce the American Academy of Environmental Engineers Certification Board granted Som Kundral certification in the specialty of Hazardous Waste Management and Site Remediation this month. Board Certified Environmental Engineers (BCEE) such as Kundral make up the top four percent of environmental engineering experts.
Kundral and his work are well established and recognized across the nation. As a rising star and SCS Engineers’ Young Professional, Kundral’s teamwork is not only recognized by his clients but by the American Council of Engineering Companies and the Environmental Business Journal with a Business Achievement Award for Groundwater and Stormwater Remediation Solution. Kundral is also a Waste360 40 Under 40 award recipient.
Well done, Som! We’re so proud of you and all of our SCS Young Professionals helping our clients build a better world.
Since 1977, WomenShelter of Long Beach has helped thousands of families overcome the trauma caused by domestic abuse. WSLB assists victims and their children by providing safe housing and supportive services, including an emergency shelter, 24-hour crisis hotline, counseling, social services support, legal and health advocacy, and much more.
SCS Engineers adopted four families in our 5th year of sponsorship. We provide gift cards for each family and hope we can go back to shopping and wrapping gifts for them next year. We wish our families and all a happy holiday season!
More community support in 2021 here.
As noted in Waste360, SWANA’s recent report, “Reducing Contamination in Curbside Recycling Programs,” shows stubborn resistance to recycling even after an intense education and enforcement campaign in two towns. A bit more than one-quarter of the households simply didn’t seem to care. While the solid waste industry finds that hard to comprehend, we’re always looking for solutions, and we don’t give up.
Here’s a simple set of recommendations from Consumer Reports published in September for using less plastic. After all, if you don’t recycle, at least try to use less plastic! Most of the recommendations will save you a lot of money and are easy to do, some of which you’re probably already doing.
Thanks to Consumer Reports for its outstanding article that we share with you here.
SCSeTools® – Developed by Landfill Gas Practitioners for Landfill Owners and Operators
The Birth of LFG Data Tracking
In the early 2000s tracking landfill gas data at facilities was anything but uniform, organized, or secure. The industry was using various methods to track data on paper forms and logbooks, then transferring it by hand into spreadsheets. Some of us used desktop database applications, but as the saying goes, necessity is the mother of invention.
From an SCS employee’s idea for demonstrating how to use landfill gas monitoring data to analyze and pinpoint system corrections, SCS DataServices® was born. In the span of several months, a team of SCS’s landfill engineers, field technicians, and technology gurus worked with client-needs to create a concept application visualizing collected landfill data on maps. Our staff field-tested it with good results, and SCS Field Services began using the application to visualize issues with wellfields that aren’t readily apparent when looking at spreadsheets.
A large SCS landfill client had seen our field staff using DataServices, asked if SCS would consider providing them with access to the application on a subscription basis. Our team adapted DataServices, added features, and continued improvements tailored for the client’s use.
As soon as secure data transfer became feasible, SCS moved to an Internet-based solution for our landfill gas practitioners. The platform called SCSeTools® holds the data collected by SCS DataServices®.
Applications and features roll out as we continually update and upgrade, incorporating ideas and improvements from our users and staff along the way. DataServices is addressing the landfill gas management needs of over 600 landfills across the US and Canada in 2021.
The keys to success follow our mission and values of maintaining close communications with our clients, field staff, engineers, and eTools support staff (all landfill gas practitioners), with the help of software engineers. Technology companies are not up at night thinking about landfill operations, but we are.
We introduce our SCS eTools landfill technology capabilities and a few of the creative and talented SCSers behind the technology in the next segment. Our speakers walk you through demonstrations of how over one-third of the landfill owners and operators in North America are increasing efficiencies using SCS eTools.
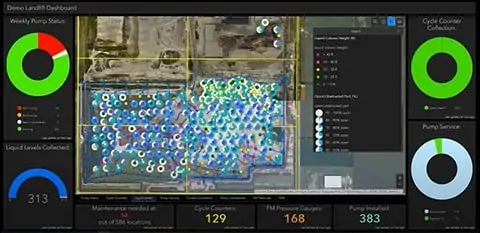
Visualizing Landfill Challenges – Shortcuts to Keeping Your Wellfield in Balance
DataServices shows the entire wellfield for any monitored parameters and zooms in on troublesome areas or wells. Results can be as simple or detailed as the landfill owners’ environmental and business needs dictate. The detailed examples here illustrate how graphs, maps, and charts help keep the wellfield in balance. We link each challenge to the description of a video demonstration.
In balance means extracting more gas for renewable energy, preventing odors and methane migration, keeps subsurface and surface conditions and workers safe. The information can help diagnose equipment conditions before they become costly, maintain regulatory compliance, and support cost estimates if the landfill is expanding or more infrastructure investment or equipment is needed.
Looking at vacuum distribution across a gas collection system – Select the system pressure map, which highlights vacuum distribution across the wellfield to show the wells with good (expected) vacuum, pressure drop over distance, and any wells unexpectantly losing vacuum. Zooming in and changing the vacuum ranges further enhances where to assign staff to troubleshoot any identified issues.
Using a methane distribution map shows whether the wells are tuned to where the landfill owner wants them. Wells may be identified below the targeted range, indicating slight over pulling; a technician can use this map to identify such issues and quickly check the identified wells. Wells identified above the desired methane tuning range indicate wells not collecting enough gas, which has consequences. These wells can be the source of odors, leachate seeps, possible lateral migration to an out of waste probe. Not sending enough fuel to a power plant or atmospheric releases can affect surface emissions monitoring.
Managing liquids – Changing waste streams and more rainfall in certain areas of the country complicates liquids management. DataServices visualizes the impacts of liquids on wells and helps landfill owners better manage a proper liquids removal program. The program will let them know how many pumps to budget for and, over time, where to relocate well dewatering pumps so that they are most efficient at removing liquids from landfills.
High-BTU Gas Plants –Filter maps help users locate wells contributing to gas dilution into renewable energy plants. It can help create punch lists for landfill staff to investigate, troubleshoot and tune. As wellfield technicians make corrections, they show on the map in real-time.
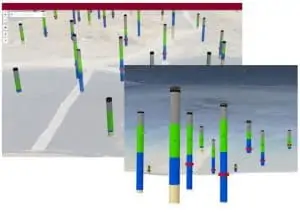
Temperature and subsurface oxidation events – Some call the condition subsurface fires, but this is a serious issue for landfills. Over-pulling wells, damaged infrastructure, and other conditions can cause oxidation events. Using a combination of temperature Parameter Maps to review wellhead temperature distribution and a Points Chart feature provides a deeper dive into the data. It provides more insight into which well or wells may be contributing to the high-temperature issues.
Locating a specific well – That’s not so easy when hundreds of wells surround you and at larger landfills. DataServices had built-in filter features to identify a single monitoring point on a wellfield map easily.
Customizing for compliance, best practices, and rules – DataServices allows monitoring points across a single site to have customized rules for each monitoring point. Rules can be for regulatory purposes, standard operating procedures, best management practices, and even site-specific preferences or any combination thereof. It is efficient to customize rule application to landfills and collection points – meaning wells, probes or ports, horizontal collectors. This customization capability helps organize and confirm regulatory compliance. It is especially salient with the 2021 EPA and state compliance changes for a single landfill or an organization with hundreds of landfills.
MobileForms – Inspection forms, blower flare station monitoring forms, load tracking from municipalities, incoming hazardous waste tracking, MRF bale counts are examples of paperless entry available. The data feeds directly from mobile phones to the supervisor and into the maintenance department, so staff can start cataloging and looking at what’s going on in real-time at several types of facilities. It’s available for regulators and inspections and helps reduce staff hours tabulating and centralizing the information. Any information historically captured on a form or log attached to a clipboard can now be captured and stored electronically. From there, it can be recovered and produced as a PDF export file or data from the forms used to trend data and help make informed operational decisions.
MobileTools – DataServices in a condensed format suitable for mobile devices. Field staff use MobileTools to save time formerly used to return to the office, transfer/transcribe the collected data and upload it to a supervisor for quality checks before storage. Technicians can now recall the last 20 readings for any given well and review trend graphs on their phones or tablets while standing adjacent to the well they have questions about and need to access the data. MobileTools also allows them to upload field data such as liquid level readings while the data is being collected. The information instantly populates into DataServices and is available for review by others on the project team.
The most valuable tools are in development now for release in 2022. ARC GIS integration developed under SCS RMC® will further enhance DataServices with even better visualization and location capabilities and provide enhanced features such as allowing landfill owners to see their well as-built information and view subsurface information about their wells.
Learn more at SCS Engineers, where we adopt our clients’ environmental challenges as our own.