

The proposed AERR rule would require nearly 130,000 facilities to report air toxics emissions directly to EPA. It would also give states the option to collect the air toxics data from industry (rather than states) and report it to EPA, provided the Agency approves their program. This proposed action would allow for EPA to annually collect (starting in 2027) hazardous air pollutant (HAP) emissions data for point sources in addition to continuing the criteria air pollutant and precursor (CAP) collection in place under the existing AERR.
Here are some key things to know about the proposed rule from the EPA website:
1. It would require air toxics (hazardous air pollutant) emissions reporting. While most states voluntarily report air toxics emissions data to EPA now, reporting is not consistent nationwide. The proposal would require many industrial facilities to report air toxics emissions data and offers states the option to report emissions on behalf of the industry sources in their states.
2. It would mean that more facilities must report emissions every year by using the same emissions thresholds every year to determine whether a facility’s detailed emissions information must be reported.
3. It would fill reporting gaps for some portions of Indian country and federal waters. The AERR proposal would require industry to report emissions for certain facilities that operate in those areas and that currently are not reported.
4. It includes provisions to limit the burden on small businesses. The proposal includes flexibilities such as allowing certain small businesses to report a facility’s total air toxics emissions instead of detailed data and exempting many collision repair shops from air toxics reporting requirements.
5. It would provide EPA information that would help the Agency improve its estimates of emissions from prescribed fires. EPA is committed to helping communities and our federal, state, local, and tribal partners manage the health impacts of smoke from wildland fires, including prescribed fires. Prescribed fire is a land management tool that can reduce the likelihood of catastrophic wildfires by reducing the buildup of unwanted fuels.
Additional Resources:
On July 1, 2023, the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (IEPA) posted and updated General NPDES Permit No. ILR00 for Industrial Storm Water Discharges (2023 General Permit). The 2023 General Permit is effective July 1, 2023, through June 30, 2028.
Multiple industry sectors must now update their site-specific Storm Water Pollution Prevention Plan (SWPPP) to comply with the 2023 General Permit. Three key updates in the 2023 General Permit are:
1-Permittees are required to submit a Notice of Intent (NOI) for renewal no later than 150 days after the 2023 General Permit is issued (i.e., by November 28, 2023).
2-Permittees must place a sign of permit coverage (except in instances where other laws or local ordinances prohibit such signage) in a safe, publicly accessible location in close proximity to the facility and include the following:
3-Benchmark sampling requirement updates, varying based on the industry sector’s Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) Code classification:
List 1 – SIC Code Groups with Updated Benchmark Sampling Constituents
Subsector C1 & C2
Subsector E1 & E2
Subsector F1 & F2
Subsector H1
Subsector L1
Subsector M1
Subsector Q1
Subsector AA1
List 2 – SIC Code Groups with New Benchmark Sampling Requirements for Reporting Purposes Only
Subsector B2
Subsector C5
Subsector D2
Subsector E3
Subsector F5
Subsector I
Subsector J3
Subsector L2
Subsector N2
Subsector O1
Subsector P1
Subsector R1
Subsector T1
Subsector U3
Subsector V1
Subsector W1
Subsector X1
Subsector Y2
Subsector Z1
Subsector AB1
Subsector AC1
Our authors are available to answer questions about the Illinois stormwater regulations. You will find state professionals for updates or filing requirements local to your operation here.
Spencer LaBelle serves as a Senior Project Engineer for our Upper Midwest Team. Spencer has prepared SWPPPs for multiple, diverse industries and operations throughout Illinois and assisted clients with SWPPP inspections from the Illinois EPA. He has diverse experience in civil/environmental consulting for stormwater and erosion control management systems, site development, and regulatory compliance.
Betsy Powers serves as a Vice President/Senior Project Manager for our Upper Midwest Team. She has over 25 years of experience in civil/environmental consulting, including erosion control and stormwater management, site development, regulatory compliance, landfill design and permitting, landfill construction, material recovery facility design, and compost facility design and permitting.
Additional NPDES and Stormwater Resources:
In degraded ecosystems, manipulating sediments can aid in recreating natural sediment processes, establishing suitable substrate conditions for aquatic life, and supporting the recovery of vegetation and wildlife. In the United States, sediment management revolves around the presence of contaminated sediment. Contaminated sediment sites pose intricate technical challenges that demand significant resources to address and mitigate the associated problems effectively.
Over the past three decades, significant progress has reduced the discharge of toxic and persistent chemicals into waterways throughout the United States. However, a persistent problem remains, characterized by elevated concentrations of contaminants in the sediment found at the bottom of rivers and harbors. The situation has raised considerable concerns about its potential risks to aquatic organisms, wildlife, and humans.
This paper delves into the technical challenges environmental engineers and consultants face in addressing and mitigating this issue, especially during waterfront remediation projects. Furthermore, he explores strategies to optimize resources to tackle the problem at hand effectively and efficiently.
Active monitoring and data collection is critical throughout the remediation process. These activities enable evaluating the chosen strategy’s effectiveness, identifying necessary adjustments, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Adaptive management approaches allow modifying or refining the sediment remediation strategy based on monitoring results and stakeholder feedback.
The utmost importance lies in choosing the appropriate remediation techniques; base the decision on site conditions, the specific contaminants present, and the desired remediation goals. After reading the paper, you may get a better idea of the options available for achieving effective and sustainable sediment remediation outcomes.

Early one Saturday morning, SCSers Chuck Houser, Luke Montague, Allison O’Neal, and me, Jen Morton, headed out to Brawley in the Imperial Valley region of Southern California. That is the desert. We had been having our usual May Gray here in SoCal when the summer can feel like winter at the coast, but the desert was a balmy 100 degrees and sunny that day.
We met with Sean Wilcock of the Imperial Valley Economic Development Corporation, one of our clients for Brownfields work, at a coffee shop in Brawley. From there, we ventured north to an area between Calipatria and Niland to see the beginning workings of a lithium extraction operation.
This region lies at the southern end of the San Andreas fault, where the motion between the North American and Pacific Plates begins to switch from strike-slip to extensional or from side-by-side to pulling apart. Where extension occurs, the crust tends to be relatively thin. Imagine pulling apart a sticky bun or taffy – the middle starts to get thinner before it breaks.
With the thinning of the crust, hot magma from the earth’s interior is closer to the surface. The heat from the magma heats the groundwater, which is A LOT beneath the Imperial Valley. And in this groundwater are minerals that, until recently, have not necessarily been worth the effort to extract from the water.
For decades energy companies have been using this super-heated water to generate electricity in the Imperial Valley. The hot water is pumped up from deep within the earth, using the steam to rotate turbines. The water is then pumped back into the aquifer.
Before our trip, Chuck and I met Tracy Sizemore, director of Battery Operations for Controlled Thermal Resources (CTR), at a San Diego Association of Geologists (SDAG) meeting learning more about the mineral resources in Imperial Valley. Chuck and I were as fascinated with that as the opportunity to see the biggest drill rig we’ve ever seen, which would be drilling an 8,000-foot well for groundwater extraction. We learned about the brine’s lithium resources (another term for the super-heated, mineral-rich groundwater).
Lithium has become a highly sought-after metal with the proliferation of electric vehicles. Given this increase in value, it is now economically feasible to extract it from the brine as part of the energy generation process. Some companies have plans to conduct the extraction in addition to electricity generation at existing geothermal plants. One company will build a separate extraction facility next to an existing plant.

CTR is planning to develop a plant that will focus primarily on the extraction of lithium, with energy generation being secondary. As Geologists, we got a tour of CTR’s prototype plant. It was fascinating to see all of the equipment and the results of the extraction process – a small bottle of lithium-rich liquid worth about $10. The extraction process also creates a sludge containing other important elements, including manganese, zinc, and even gold and silver. The plan is to sell the sludge to another company to extract the additional economic elements.
The process of extracting lithium in this manner is sustainable and much cleaner than traditional mining methods. It is also considered carbon-neutral. The new plant will generate enough electricity to power it 100%, with enough left over to power a battery manufacturing facility next door after its construction.
CTR’s lithium extraction process expects to bring 1,400 jobs to the area, with another 4,000 jobs once the battery plant is up and running. With the influx of workers, the Imperial Valley needs more infrastructure, housing, and services, so it is supporting economic growth.
In the fall, we plan to return to CTR’s facility to see the enormous rig drilling the 8,000-foot well!
Meet the Author – Jen Morton, Professional Geologist and SCS Project Manager
Consider a position with the finest pure-environmental firm in North America!
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is proposing to designate perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), including their salts and structural isomers, as hazardous substances. The proposed rule published in the Federal Register designates two per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (collectively, PFAS) constituents as CERCLA Hazardous Substances. While this is a small subset of PFAS constituents, PFOA and PFOS are reportedly the most commonly used and likely to be detectable. Additional PFAS compounds are certainly on the horizon for consideration by EPA and, in fact, an Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking was issued by EPA in April of 2023 to seek input for seven additional compounds for hazardous substance designation.
What Could This Mean For Property Transactions and Real Estate Development?
When the CERCLA hazardous substance rule becomes final (anticipated in 2023 or 2024), it will be mandatory to consider these PFAS constituents when performing Phase I Environmental Site Assessments (ESAs) to identify Recognized Environmental Conditions (RECs) in connection with a property. Because of the ubiquitous use of PFAS, often called “forever chemicals,” in residential, commercial, and industrial products, some Environmental Professionals are concerned that PFAS-related RECs will be commonplace.
In their recent paper, “How Will EPA’S Proposed CERCLA Hazardous Substance Designation of PFOA and PFOS Impact the Environmental Due Diligence Practice?” Jeff Marshall, PE, and Mike Miller, CHMM, discuss the anticipated impacts of the PFAS rule on environmental due diligence. Depending on the former uses, the number of RECs, and ESA results, some sites are more likely to feel the impact on the potential value of a property.
As our PFAS knowledge continues to evolve, so will applying this knowledge to the environmental due diligence practice and, ultimately, real estate conditions. Read the technical paper to understand the terminology and types of properties more likely at risk.

Michael J. Miller, CHMM – Vice President. Mr. Miller is a Vice President and the practice leader for the Environmental Services Practice for SCS offices in the Central region. He also serves as an SCS National Expert for Environmental Due Diligence. He supports firm operations throughout the United States related to Phase I and II Environmental Site Assessments and the completion of large portfolios and complex site assessments. A Certified Hazardous Materials Manager (CHMM) since 2009, Mike has more than 28 years of experience in environmental management and consulting with an extensive background in RCRA-related matters and industrial compliance, planning, and permitting.
Additional Real Estate Resources:
Environmental justice is integrated into State and Federal environmental agency policy-making, thus impacting inspections and enforcement across the nation. While specifics are evolving quickly in each state, staying abreast of these basic requirements for the key environmental permits and plans listed here is best, especially if you have multiple facilities in multiple states.
We recommend this quick read to run through a checklist to decide if your facility is ready or may need an internal audit. For this article, we’re using Illinois and standard Federal requirements.
Being well-prepared for an inspection saves time and expense but will also support your company’s relationship with the regulatory agency and promote better outcomes and reduced risk of enforcement actions.
Deficiencies noted during an inspection can be a catalyst for additional inspections among non-EJ-located facilities.
Manufacturers in environmental justice areas denoted within each state can prepare for regulatory review and inspection by conducting internal or external audits of key environmental permits and plans to evaluate compliance with state and local regulations.
Additional Information:
The Maryland Department of the Environment (MDE) reminded all stakeholders that enforcing the state’s new food diversion regulations begins April 1, 2023. The law governing these regulations, entitled “Solid Waste Management – Organics Recycling and Waste Diversion – Food Waste,” was enacted on January 1, 2023.
Diversion reduces waste at final disposal sites, such as landfills and incinerators. Food residuals include edible and nonedible materials derived from pre- and post-consumer vegetables, fruits, grains, dairy products, and meats.
A facility must implement food diversion techniques if it generates at least two tons of food residuals per week. Affected facilities include businesses, public and private schools, supermarkets, and government-run cafeterias.
SCS Engineers advises facility owners and operators to review MDE’S Determination of Applicability to determine if they are subject to enforcement. MDE strongly recommends that facility owners and operators submit a Waiver Application Form if they believe they are not subject to enforcement or cannot comply with the regulations.
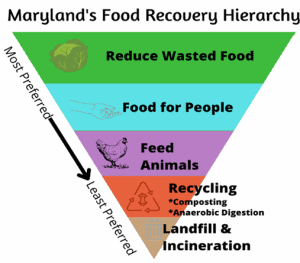
Maryland generates an estimated 1.86 million tons of compostable materials and 927,926 tons of food waste annually. Although a major waste component, only a small amount is reused or recycled. What remains ends up being disposed of in landfills or incinerated. Diverting edible foods can help address the 1 in 8 (12.5%) food-insecure Marylanders. Preventing food scrap and organics disposal using methods such as composting or donating to those in need conserves energy and resources, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
SCS Engineers periodically prepare SCS Technical Bulletins – short, clear summaries of rules, plans, and standards. In 2021, ASTM International published an updated consensus guidance document for evaluating environmental conditions at properties involved in commercial real estate transactions.
This SCS Technical Bulletin for the revised E1527-21, Standard Practice for Environmental Site Assessments: Phase I Environmental Site Assessment Process addresses definitions and terminology, clarifies industry practice for the historical records review of the subject and adjoining properties, and provides for updates and additions to appendices, report outlines, and other collateral.
Our updated edition now includes the revised guidance speaks to the business risk associated with emerging contaminants, such as Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
Read, share, download the A New Standard Practice for Phase I Environmental Site Assessments Tech Bulletin here.
For more information about Environmental Due Diligence, please visit our website.
USEPA recently issued Effluent Guidelines Program Plan 15, which includes a focus on PFAS discharges from multiple categories. In conjunction with Plan 15, EPA has determined that revisions to the effluent guidelines and standards for the Landfills Category (40 CFR part 445) are warranted. See Section 6.3.3 of the Plan. Here are a few excerpts regarding landfill leachate:
Landfill leachate and wastewater treatment planning and resource information are available here.
On December 24, 2022, the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (PADEP) published the renewed NPDES General Permit for Discharges of Stormwater Associated with Industrial Activity (PAG-03). This permit covers stormwater discharges from industrial facilities such as manufacturing facilities, landfills, scrap yards, and bus terminals.
The new permit term will cover operations from March 24, 2023 (effective date) to March 23, 2028 (expiration date). If PADEP receives an NOI by March 23, 2023, an existing PAG-03 permittee can continue to discharge under the reissued PAG-03. The application forms and instructions are available from the PADEP eLibrary.
Beginning in 2024, the due date of the Annual Report and NOI fee annual installment payment will be by March 23 each year. For existing permittees, the due date for the NOI fee installment in 2023 and the annual report covering 2022 will be May 1, 2023.
Analytical requirements for monitoring stormwater discharges are established in an appendix to the General Permit for each industrial sector. A monitoring requirement for Total Nitrogen and Total Phosphorous was added to each Appendix. Other changes made are to monitoring and Benchmark Value parameters for individual sectors. Target Quantitation Limits (TQLs) are established for analytical parameters, and permittees must use labs that can meet the TQLs to comply.
The new permit increases response levels for continual exceedances of Benchmark Values, concentrations of pollutants that serve as a threshold for evaluating whether site Best Management Practices effectively control stormwater pollution. Two or more consecutive monitoring period exceedances of Benchmark Values trigger the requirement to develop and submit a corrective action plan, implement additional controls, or apply for an individual permit if notified by PADEP.
Monitoring under the renewed permit commences with the July 1 – December 31, 2023 monitoring period. Until July 1, 2023, permittees should continue monitoring for parameters in their existing General Permit.
These are not the only changes made to the General Permit. Please contact for updates in other states or commonwealths and Denise Wessels at (610) 382-3050 if you need help preparing the NOI to reapply for the permit or to maintain compliance with permit terms in Pennsylvania.